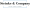Overview
This article dives into the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE), something every expatriate should definitely know about. Did you know that U.S. citizens living abroad can potentially exclude up to $130,000 of their foreign earned income from U.S. taxes? It’s a pretty big deal!
Understanding the eligibility criteria and filing requirements is crucial if you want to maximize your tax benefits while staying compliant with IRS regulations. So, let’s break it down together and make sure you’re on the right track!
Introduction
Understanding the ins and outs of the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE) can really make a difference for U.S. expatriates looking to get the most out of their tax situations while living overseas. This tax provision lets folks exclude a good chunk of their foreign earnings from U.S. taxes, which could mean saving thousands of dollars each year! But let’s be real—figuring out the eligibility requirements and application processes can feel pretty overwhelming.
So, how can expatriates make the most of this benefit without stumbling into common traps? In this article, we’ll dive into ten real-life examples of the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion, offering valuable insights and practical tips for expats who want to maximize their financial perks.
Steinke and Company: Expert Guidance on Foreign Earned Income Exclusion for Expats
At Steinke and Company, we take pride in offering expert advice on a foreign earned income exclusion example specifically designed for U.S. expatriates, especially those in service-oriented professions. Our proactive tax planning services make tax season a breeze—smooth, accurate, and stress-free. This way, our clients can navigate the intricate world of tax compliance while maximizing their benefits under the foreign earned income exclusion example. With a dedicated team of experienced Enrolled Agents and CPAs, we ensure that expatriates fully grasp their eligibility criteria and the detailed steps to effectively claim this exclusion.
Take Sarah, for instance. She kept her home in London during 2024, which means she qualifies under the Bona Fide Residence Test, allowing her to exempt a significant portion of her earnings from U.S. taxes. On the flip side, there’s Robert, who returned to the U.S. before completing a full tax year overseas. He might find he doesn’t qualify for the foreign earned income exclusion, highlighting the importance of thoughtful planning and professional support.
We emphasize the necessity of submitting Form 2555 to request the foreign earned income exclusion example, making it clear that this exemption isn’t automatic. Plus, we help clients navigate the often tricky state tax obligations, as many states have rules that let individuals break tax residency when relocating abroad. We also assist clients with accurate currency conversion using IRS-approved exchange rates, which is crucial for providing a foreign earned income exclusion example. And here’s a handy tip for U.S. citizens living abroad: you automatically get a 2-month extension until June 15 to file your taxes—definitely something for expats to keep in mind!
As Mel Whitney, one of our skilled Enrolled Agents, puts it, "The Bona Fide Residence Test applies to U.S. citizens and resident aliens who are bona fide residents of a foreign country for an uninterrupted period that includes an entire tax year (January 1 - December 31)." By providing regular consultations and strategic planning sessions, we help clients spot opportunities to lessen their tax burdens and boost overall business performance. This makes Steinke and Company a trusted ally for small business owners tackling the challenges of international taxation.

Foreign Earned Income Exclusion: A Key Tax Benefit for U.S. Expats
The foreign earned income exclusion example is a game-changer for U.S. citizens and resident aliens living abroad. It lets you exclude up to $130,000 of foreign earned income from U.S. taxes for the tax year 2025. If both you and your spouse qualify, that could mean a whopping $260,000 excluded! This exclusion really helps lighten the tax load for expatriates, making it something every American working outside the U.S. should think about.
Did you know that around 9.5 million U.S. citizens live overseas? Many of them benefit from a foreign earned income exclusion example, which can lead to substantial reductions in their overall tax bills. To take advantage of this, you'll need to file IRS Form 2555 and meet either the Physical Presence Test or the Bona Fide Residence Test. Tax consultants often say that a foreign earned income exclusion example can be a real game-changer for expatriates, allowing you to hold onto more of your hard-earned money while staying compliant with U.S. tax laws.
For instance, if you meet the qualifications for the foreign earned income exclusion example, you can effectively lower your taxable income. This means more funds to invest in your local community or save up for future adventures! Understanding and applying a foreign earned income exclusion example is key for U.S. expatriates looking to improve their financial situation while enjoying life overseas.
Physical Presence Test: Qualifying for the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion
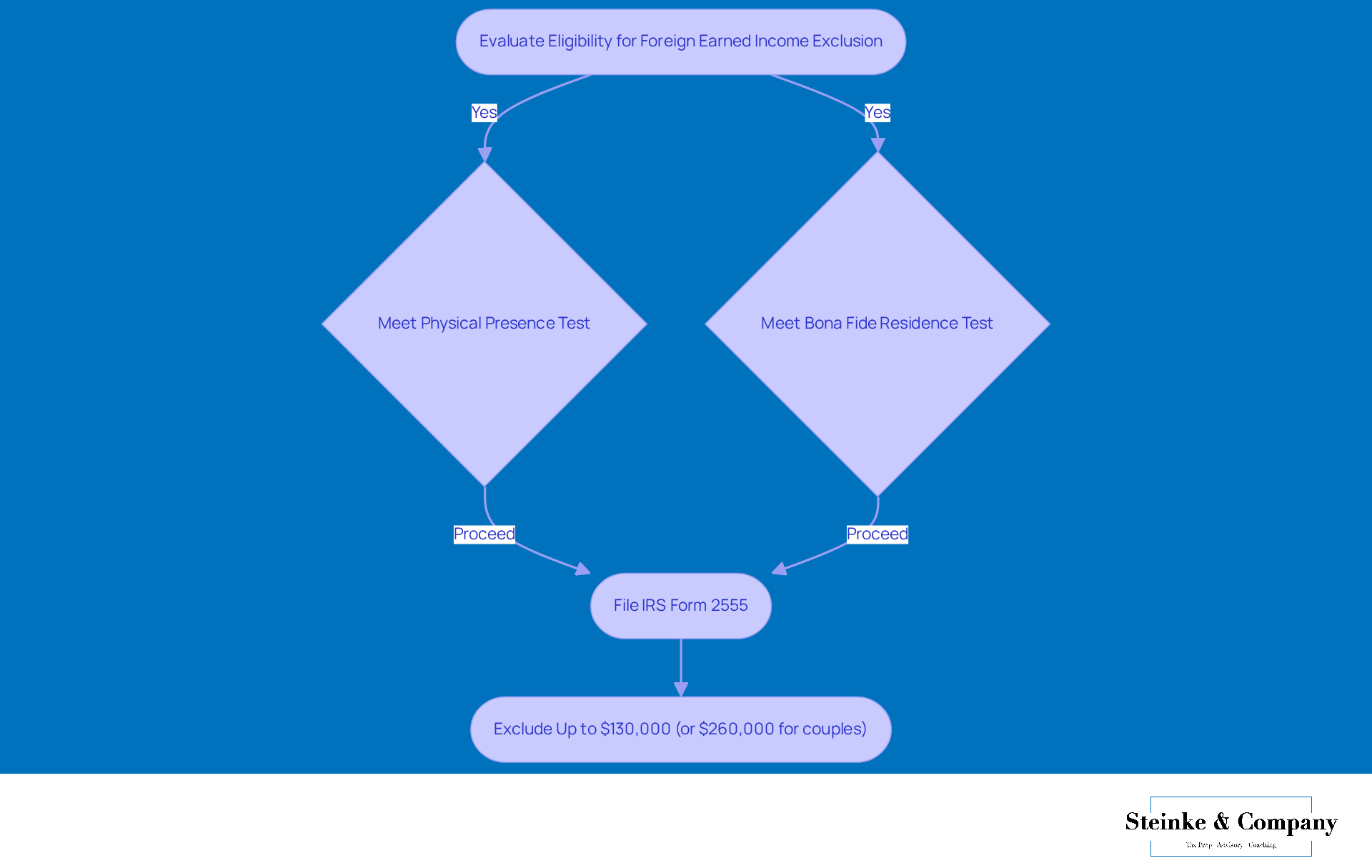
If you're looking to benefit from the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion, you’ll need to ace the Physical Presence Test. This means you have to be physically present in a foreign country for at least 330 full days within a 12-month period—yep, that’s about 91% of the year! This requirement is super important because it can lead to some significant tax savings. So, keeping precise records is key; make sure to document your travels to back up your claims.
Take Jennifer, for instance, as a foreign earned income exclusion example. She was working remotely from Colombia and spent 338 complete days in other countries, which put her over the limit and served as a foreign earned income exclusion example. Aisha did even better, clocking in 342 days abroad and meeting the criteria too! Just remember, days spent in international waters or back in the U.S. don’t count toward that 330-day total. Keeping detailed travel records—like airline tickets and hotel receipts—is essential to show you’ve met the Physical Presence Test.
As tax specialists often remind us, clear documentation not only supports your claims but also makes the tax filing process smoother. This is especially helpful for those living overseas who want to take full advantage of the foreign earned income exclusion example as a valuable tax provision. And if you find yourself needing a little extra time, consider filing for a tax extension, as Sophia suggests. This way, you can ensure you have enough time to prepare your returns and successfully claim that Foreign Earned Income Exclusion!
Bona Fide Residence Test: Understanding Residency Requirements for FEIE
The Bona Fide Residence Test is a key player for foreign residents looking to qualify for a foreign earned income exclusion example. So, what does it really mean? Well, it’s all about proving that you’ve set up a permanent home in another country. This means you need to live there for a stretch—usually a full tax year—without any plans of heading back to the U.S. for good.
Understanding this foreign earned income exclusion example is crucial if you want to ensure you meet the criteria for those tax benefits. After all, who doesn’t want to save a bit on taxes while enjoying life abroad? Just remember, it’s not just about living there; it’s about making it your home. So, have you thought about how this might apply to your situation?
What Counts as Foreign Earned Income: Key Definitions for Expats
Foreign earned earnings include wages, salaries, professional fees, and other forms of compensation for services rendered in a foreign country. If you’re an expat, it’s super important to distinguish foreign earned revenue from other types, especially investment income, which doesn’t qualify for the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE). Misclassifying your earnings can mean missing out on tax benefits and even facing penalties.
Take Sarah as a foreign earned income exclusion example. As a U.S. citizen working in London, she qualifies for the foreign earned income exclusion due to her earned income. On the flip side, Harry, who’s receiving dividends from his U.S. investments, doesn’t qualify. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for making the most of your tax advantages and staying in line with IRS regulations.
As tax advisors often say, "Only earned income—like salary, wages, and self-employment income from work performed in a foreign country—qualifies." This clarity not only helps with tax preparation but also makes it easier for foreign residents to navigate their financial responsibilities effectively. So, keep these points in mind as you plan your finances!
Foreign Housing Exclusion and Deduction: Maximizing Tax Benefits for Expats
If you’re living overseas, you might be eligible for the Foreign Housing Exclusion or Deduction, as well as a foreign earned income exclusion example. This handy benefit allows you to exclude or deduct certain housing expenses while you’re abroad, like rent, utilities, and other related costs.
To really make the most of these benefits, it's a good idea to keep detailed records of your housing expenses. And don’t hesitate to reach out to tax experts—they can help ensure you’re following all the IRS rules.
Have you thought about how you’re tracking your expenses?
FEIE vs. Foreign Tax Credit: Choosing the Best Tax Strategy for Expats
If you're an expat, you’ve got some choices to make when it comes to taxes. You can choose between the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion example or the Foreign Tax Credit. The foreign earned income exclusion example shows that it is a great option if you’re raking in some serious foreign earnings. On the other hand, if you’re dealing with hefty foreign taxes, the Foreign Tax Credit might just be your best friend.
Now, figuring out which route to take can feel a bit overwhelming, right? That’s why it’s super helpful to take a good look at your own financial situation and maybe chat with a tax expert. They can help you navigate through the options and find the best fit for your unique circumstances. So, what do you think? Have you considered which option might work better for you?
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Claiming the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion
When it comes to claiming the foreign earned income exclusion example, overseas workers can sometimes trip up in a few common areas. Maybe they miss the residency requirements, misclassify their earnings, or don’t keep enough records. To steer clear of these pitfalls, it’s super helpful for foreign workers to get acquainted with IRS guidelines and double-check their paystubs for accurate income reporting.
Keeping thorough documentation is key—not only does it back up their claims, but it also comes in handy if the IRS decides to take a closer look. For small agency owners, it’s important to know their rights during an audit and think about reaching out for professional tax advice. This way, they can ensure their claims are on point and compliant. Taking this proactive approach can really help bolster their financial stability and keep everything above board.
Importance of Professional Tax Advice for Expats Navigating FEIE
Navigating the complexities of the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE) can be quite the task for expatriates, right? That’s why professional tax advice is like gold—it helps ensure you’re on the right side of IRS regulations while maximizing those tax benefits. Tax experts can whip up customized strategies that fit your unique situation, making it easier for you to make informed choices and dodge those costly mistakes.
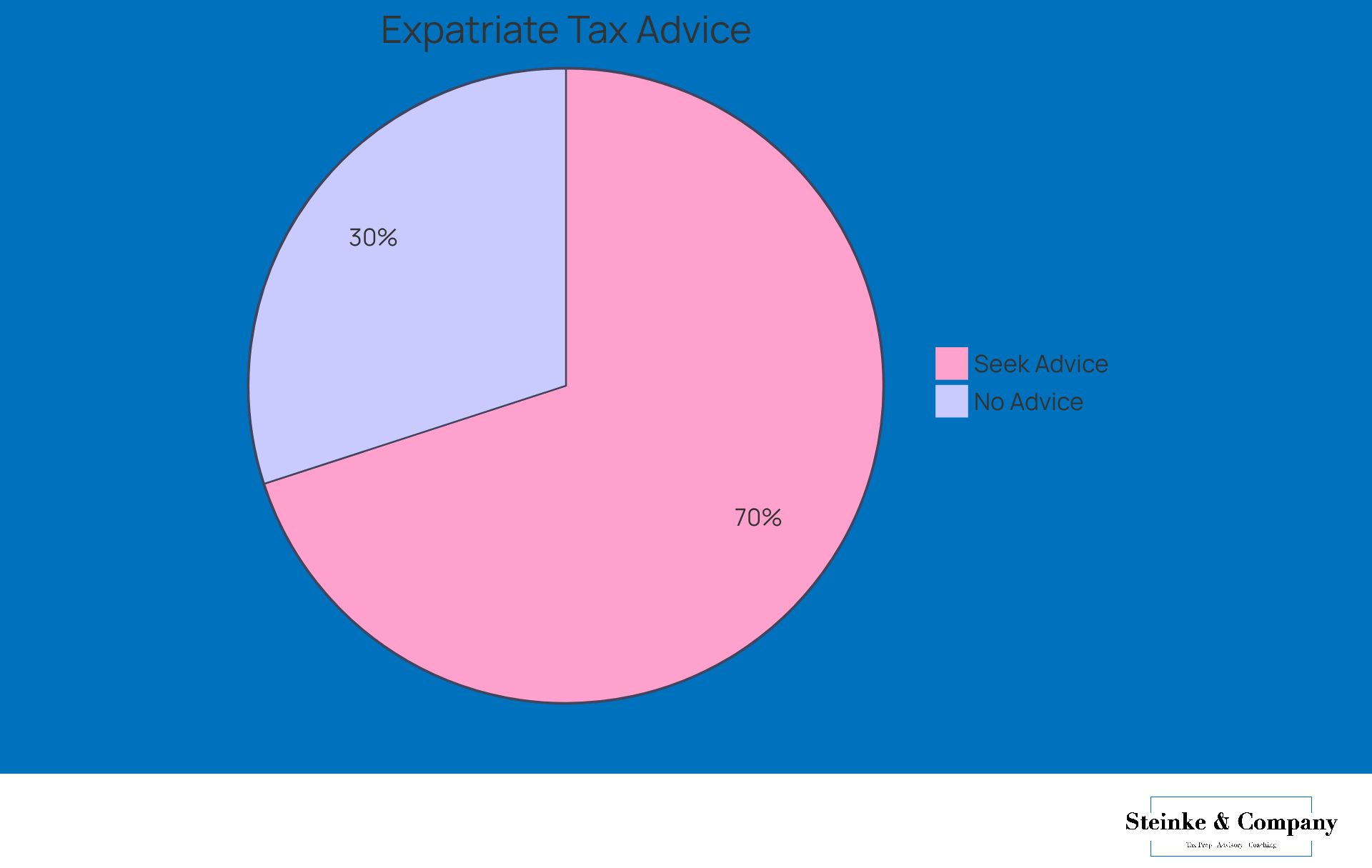
In fact, did you know that around 70% of expatriates turn to professional tax advice to help them through these intricate tax rules? It’s true! For instance, tax experts can provide a foreign earned income exclusion example by helping you exclude up to $126,500 of foreign earned income from taxation in 2024, which is a nice bump from the $120,000 you could exclude in 2023. That’s a significant reduction in your taxable earnings!
But that’s not all—they also help you spot and use foreign tax credits, which can be a game changer in tackling double taxation issues. Just think about the potential fallout from tax errors, like penalties or even audits. This really highlights why hiring a tax professional is so important. By tapping into the expertise of tax advisors, you can not only ensure compliance but also boost your overall financial well-being.
As one tax advisor put it, 'Ultimately, this decreases the odds of tax return mistakes—and subsequently, amended return requests, penalties and fines, and audits.' So, why not take that step and get the help you need?
Additional Tax Benefits for Expats: Beyond the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion
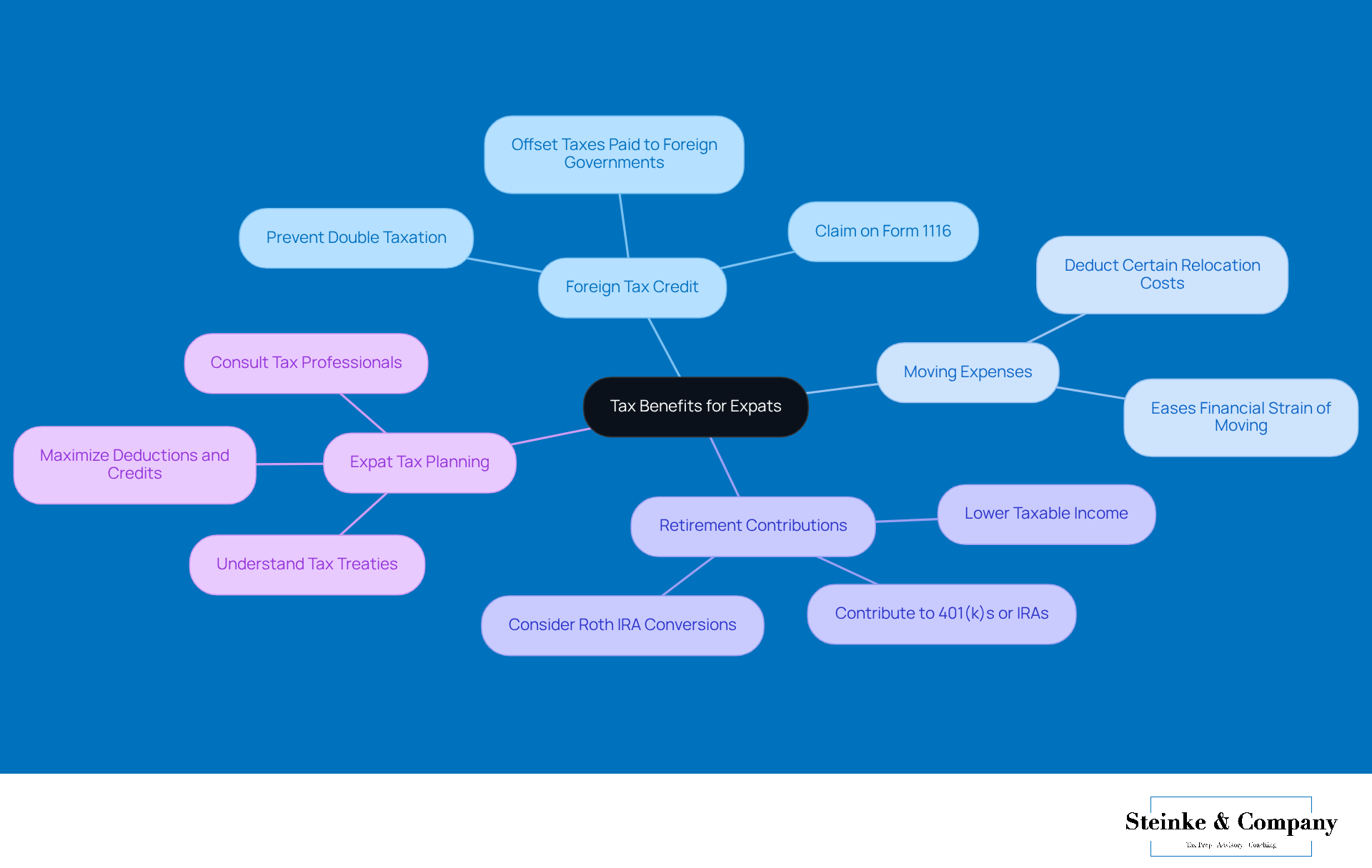
When it comes to managing taxes as an expatriate, there’s more to explore beyond just the foreign earned income exclusion example. One key option is the Foreign Tax Credit (FTC). This handy credit allows you to offset taxes paid to foreign governments against your U.S. tax liabilities, which can help you avoid being taxed twice on the same income. It’s no wonder that many expatriates take advantage of the FTC—it's a vital part of smart international tax planning!
But that’s not all! If you’ve recently moved overseas, you might be able to deduct certain moving expenses, easing some of the financial strain that comes with relocating. Plus, don’t forget about contributions to retirement accounts like 401(k)s or IRAs. These can be a great way to lower your taxable income while also building up your savings for the future.
Tax pros really stress the importance of understanding these additional benefits. As one expert put it, "Maximizing available deductions and credits is crucial for expatriates to enhance their financial well-being while living abroad." So, by strategically using the FTC and other deductions, you can really boost your overall tax situation. It’s all about staying compliant while making the most of your financial opportunities!
Conclusion
The foreign earned income exclusion is a fantastic opportunity for U.S. expatriates, letting them significantly cut down their taxable income while living abroad. By getting a handle on the eligibility criteria—like the Physical Presence Test and the Bona Fide Residence Test—expatriates can navigate the sometimes tricky waters of U.S. tax laws and truly make the most of this tax benefit.
Throughout this discussion, we’ve seen how folks like Sarah and Robert deal with the implications of these tests. Their stories highlight just how important it is to plan strategically and seek professional guidance. Plus, we can’t overlook the necessity of keeping accurate records and considering additional tax strategies, such as the Foreign Tax Credit, which can really boost the financial well-being of expatriates.
In the end, tapping into the foreign earned income exclusion and its related benefits can lead to some serious tax savings. Working with tax professionals can offer personalized advice, helping ensure compliance while maximizing opportunities for financial growth. As expatriates set off on their international adventures, understanding these tax advantages is key to securing their financial future and enjoying life abroad.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion?
The Foreign Earned Income Exclusion allows U.S. citizens and resident aliens living abroad to exclude up to $130,000 of foreign earned income from U.S. taxes for the tax year 2025. If both spouses qualify, they could exclude up to $260,000.
Who qualifies for the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion?
To qualify for the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion, individuals must meet either the Physical Presence Test or the Bona Fide Residence Test.
What is the Physical Presence Test?
The Physical Presence Test requires that an individual be physically present in a foreign country for at least 330 full days within a 12-month period, which is about 91% of the year.
What is the Bona Fide Residence Test?
The Bona Fide Residence Test applies to U.S. citizens and resident aliens who are bona fide residents of a foreign country for an uninterrupted period that includes an entire tax year (January 1 - December 31).
How do I claim the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion?
To claim the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion, you must file IRS Form 2555 and provide necessary documentation to demonstrate your eligibility.
What are the benefits of the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion for expatriates?
The Foreign Earned Income Exclusion can significantly reduce the overall tax bill for expatriates, allowing them to retain more of their income for savings or investments.
What should I keep in mind regarding state tax obligations while living abroad?
Many states have rules that allow individuals to break tax residency when relocating abroad, so it's important to understand your state's specific regulations.
How can I ensure my currency conversion is accurate for tax purposes?
Accurate currency conversion using IRS-approved exchange rates is crucial for claiming the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion.
Is there an extension for filing taxes for U.S. citizens living abroad?
Yes, U.S. citizens living abroad automatically receive a 2-month extension until June 15 to file their taxes.
What documentation should I maintain to support my claims for the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion?
Keep detailed records of your travels, such as airline tickets and hotel receipts, to support your claims for the Physical Presence Test.