Overview
This article dives into the limitations of passive activity losses for small businesses and shares some key insights on how to navigate these tax regulations. It's super important to grasp those IRS rules, keep your records in check, and think about strategies like material participation and income thresholds. Why? Because informed tax planning can really make a difference in your business's financial health.
So, have you ever wondered how understanding these nuances could impact your bottom line? By staying informed and proactive, you can optimize your tax outcomes. Remember, it’s all about making those rules work for you! Let's tackle this together and ensure your business thrives.
Introduction
Understanding the complexities of passive activity loss limitations is super important for small businesses trying to navigate the tricky world of tax compliance. With some recent changes in tax regulations—think updates to reporting requirements—small business owners are facing both challenges and opportunities when it comes to managing their tax liabilities effectively. So, how can they take advantage of these insights to optimize their financial strategies and ensure compliance while keeping their tax burden as low as possible?
In this article, we’ll dive into ten key insights that will empower small businesses to navigate the nuances of passive activity loss limitations with confidence. Let’s explore together!
Steinke and Company: Expert Tax Compliance for Passive Activity Loss Limitations
At Steinke and Company, we’re all about providing tailored tax compliance solutions for small businesses, especially when it comes to understanding and managing passive activity loss limitation. Our team of seasoned professionals is here to make sure you’re in the loop about the ins and outs of tax regulations. This knowledge is crucial for service-oriented businesses that often face unique challenges with tax reporting and deductions related to passive activity loss limitation.
Now, with the recent updates to the 1099-K reporting requirements—where transactions over $600 need to be reported—it’s more important than ever for small businesses and gig economy taxpayers to keep their records straight and know what their tax obligations are. That’s where we come in! We offer proactive tax planning services that help you navigate these complexities, ensuring you select the right accounting methods and strategies that not only support your growth but also help lighten your tax load.
For example, we always encourage our clients to maintain detailed records of all income-generating activities and related expenses. Trust us, this can have a significant impact on your overall tax liability. So, are you ready to take control of your tax situation? Let’s work together to make tax season a breeze!
IRS Form 8582: Key to Reporting Passive Activity Losses
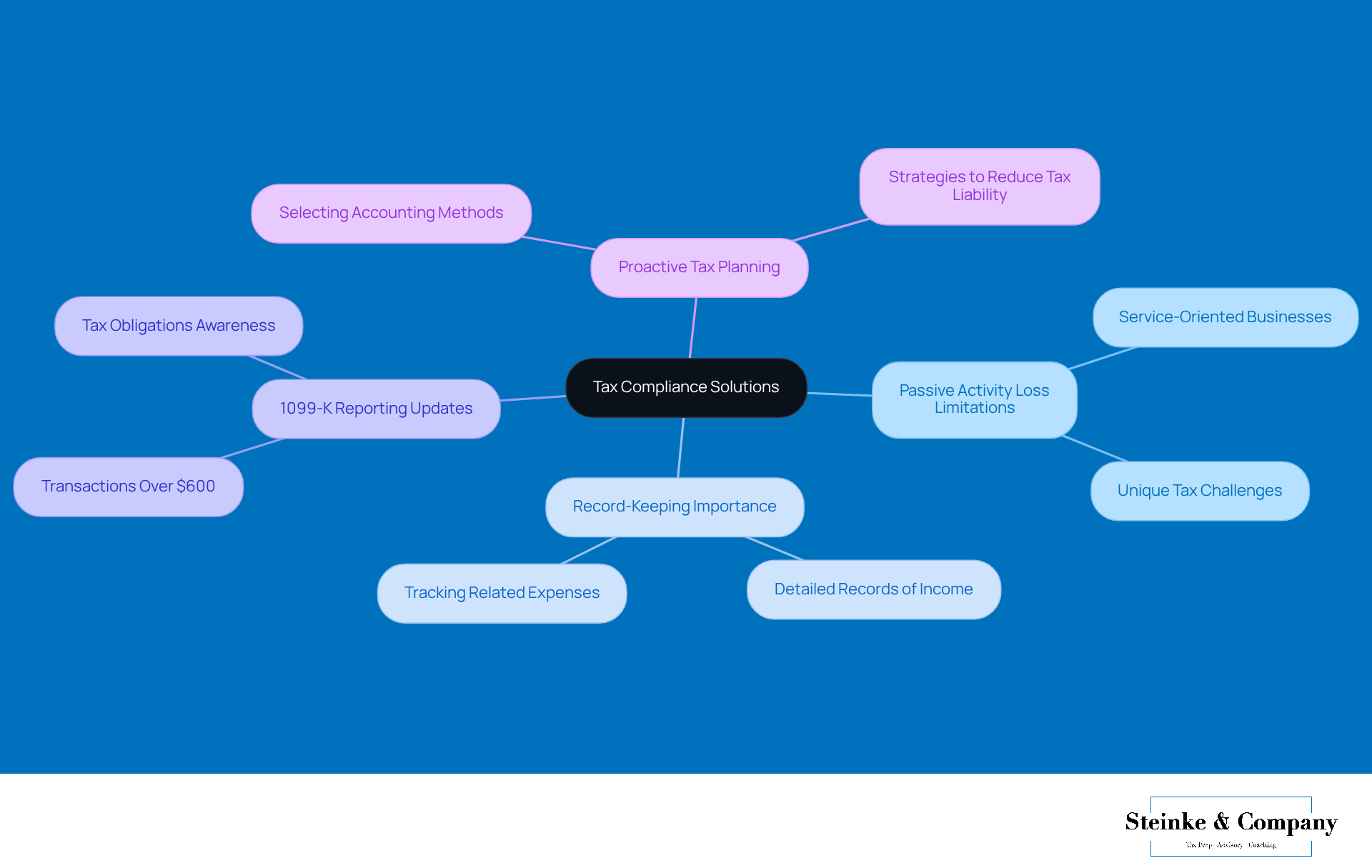
Hey there! Let’s talk about IRS Form 8582, the go-to document for reporting those pesky deficits related to passive activity loss limitation. This form is super helpful for taxpayers who want to figure out how much non-operating deductions they can claim under the passive activity loss limitation in a given tax year. It asks for all sorts of details about those inactive activities, like income and deficits, and it’s crucial for keeping things in line with the passive activity loss limitation and IRS regulations.
If you’re a small business owner, it’s really important to get the hang of filling out this form correctly. Why? Well, it can save you from penalties and help you make the most of your deductions! So, take a moment to familiarize yourself with it—your wallet will thank you later!
Material Participation: Understanding Its Role in Passive Loss Deductions
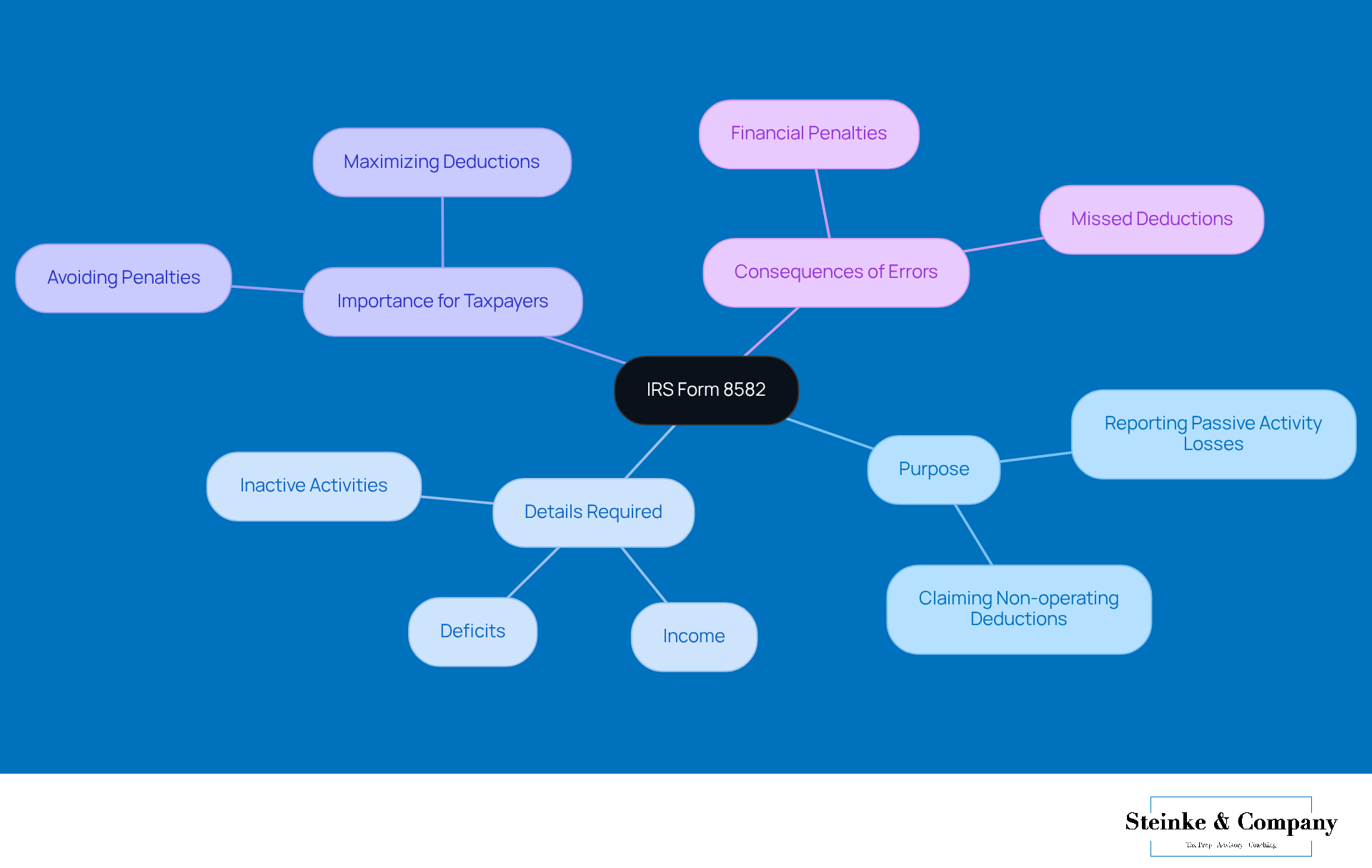
Material involvement is super important when it comes to figuring out if a taxpayer can snag those non-active deduction benefits. To qualify, taxpayers need to show they’re really engaged in some economic activity—usually by clocking in over 500 hours in a year. This is especially key for small business owners, as the passive activity loss limitation directly impacts their ability to write off losses from non-active ventures.
Did you know that only about 20% of small business owners consistently hit the material participation mark? That’s a big deal! This really highlights why keeping good records is so crucial. Tax pros emphasize that having accurate records can back up claims of material participation, and believe me, it can make a huge difference in your tax bills.
For instance, if you’re a small business owner managing a rental property and you diligently track your hours, the passive activity loss limitation could allow you to offset those inactive losses against your other income. That’s a win for your overall tax situation! So, by getting a handle on these requirements, small business owners can really fine-tune their tax strategies and stay on the right side of IRS regulations.
Special Allowance for Rental Real Estate: A Key Exception to Passive Loss Rules
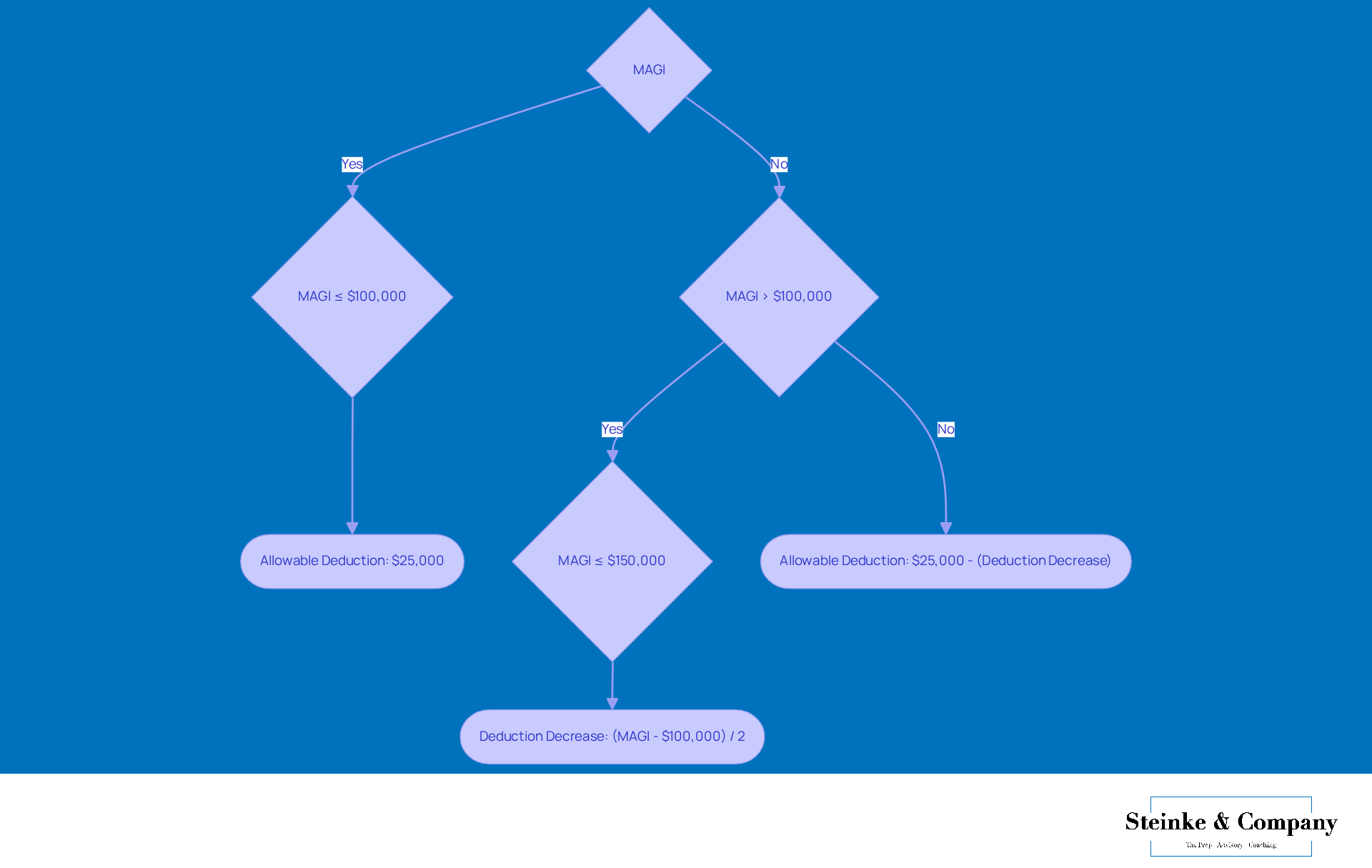
Did you know that the IRS offers a unique deduction for rental real estate activities? It’s true! If you qualify, you can subtract up to $25,000 in non-active expenses against your non-active income—provided your modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) is under $100,000. This is a fantastic perk for small landlords and real estate investors, as it helps offset losses that might otherwise be constrained by the passive activity loss limitation.
But here’s the catch: this deduction starts to phase out once your MAGI exceeds $100,000 and is completely gone at $150,000. For example, let’s say you’re a small landlord with $15,000 in rental expenses and $10,000 in rental income. You can use this deduction to significantly lower your taxable income—potentially reducing your tax bill by allowing you to deduct up to $25,000 against your ordinary income.
Understanding the criteria for the passive activity loss limitation is really important, especially if you want to save on taxes. It can make a big difference, particularly for those who are actively involved in their rental activities. Many tax consultants recommend keeping your documentation organized and seeking expert advice to make the most of these deductions. And don’t forget about Form 8582! It’s crucial for calculating and reporting non-active activity deficits, so having a handle on the passive activity loss limitation can really help you out.
Passive Loss Limitations: Understanding the Rules and Their Impact
Restrictions on deductions can really hinder taxpayers' ability to offset those pesky deficits from inactive activities against other income because of the passive activity loss limitation. Typically, passive losses are only able to offset passive income, and any leftover losses? They just sit there, suspended, waiting to be carried forward to future tax years. It’s super important for small business owners to understand the passive activity loss limitation because it can seriously affect their overall tax strategy and financial planning.
And hey, while we’re at it, let’s not forget about underpayment penalties! Small business owners need to keep an eye on how these restrictions might interact with those penalties, especially if you're not quite hitting your estimated tax obligations. So, what’s the expert’s advice? Regularly check in on your non-active activities and tax situation. This can really help boost your financial results and keep those IRS audits at bay!
Exceptions to Passive Activity Loss Rules: What You Need to Know
Hey there, taxpayers! It’s crucial to know that there are some exceptions to the passive activity loss limitation rules that can significantly impact your tax bills. For instance, if you’re a real estate pro, you can actually subtract losses without the usual limits—provided you meet certain criteria, like being actively involved in your rental activities for over 750 hours in a tax year. This means you can treat those rental losses as nonpassive, which can lead to some pretty sweet tax perks.
Now, let’s talk about how your level of involvement can also open doors to exceptions. If you’ve got a rental property where guests typically stay for 7 days or less, it might just qualify as an active trade. This could mean better tax treatment for you! Tax advisors often stress how vital it is to grasp these exceptions, particularly the passive activity loss limitation, because they can really help small business owners fine-tune their tax strategies and snag more deductions.
Did you know that a lot of real estate experts are making the most of these non-active deduction exceptions? They’re using their status to boost their tax situations. Plus, there’s been a lot of buzz lately about the evolving landscape of inactive deduction allowances, which is something every real estate expert should keep an eye on. So, by staying informed and organizing your strategies wisely, you can tackle those non-active setbacks and reduce your overall tax burden. Sounds good, right?

Income Limits for Passive Losses: Key Considerations for Taxpayers
Income thresholds really matter when it comes to figuring out how much you can deduct for those non-active expenses. If your modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) is $100,000 or less, you can subtract up to $25,000 in non-active deductions from your ordinary income.
But here's the catch: if your MAGI falls between $100,000 and $150,000, that deduction starts to phase out. For every $2 you earn over the $100,000 mark, your allowable deduction goes down by $1.
It's a bit of a balancing act, right? Understanding the passive activity loss limitation is crucial for effective tax planning, so keep it in mind as you navigate your finances!
Carrying Over Passive Losses: Strategies for Future Tax Years
When inactive deductions pile up beyond inactive earnings, those extra deductions don’t just vanish—they get postponed and carried over to future tax years. This carryover can be a game-changer for managing tax liabilities, especially in relation to passive activity loss limitation and offsetting future passive income. Small businesses can really take advantage of this with a few smart strategies:
- Keep Detailed Records: It’s super important to maintain meticulous records of those carried-over losses. Not only does this help you stay compliant with the passive activity loss limitation, but it also simplifies tracking potential offsets against future income.
- Develop a Proactive Tax Strategy: Getting ahead with tax planning means you can predict future income streams and adjust your carried-over deficits accordingly. This kind of foresight can lead to some serious tax savings.
- Consult with Tax Advisors: Don’t underestimate the value of insights from tax professionals. They can offer tailored strategies for managing your carried-over deficits and help you spot the best opportunities based on your unique financial situation.
- Look at Real-World Examples: Plenty of small businesses have successfully used carried-over dormant deficits. For instance, a small real estate company might carry forward a $40,000 non-operating deficit from one year and apply it to future non-operating gains, significantly reducing their taxable income.
- Strategic Timing: Timing is everything! Knowing when to recognize unearned income can really boost the effectiveness of your carried-over deficits. By scheduling your revenue recognition wisely, you can maximize the offsetting benefits of those deficits.
By putting these strategies into action, small businesses can not only manage their tax obligations more effectively but also improve their financial health through the smart use of carried-over non-operational deficits, considering the passive activity loss limitation. So, why not start thinking about how you can implement these tactics in your own business?

At-Risk Rule for Passive Losses: Navigating the Limitations
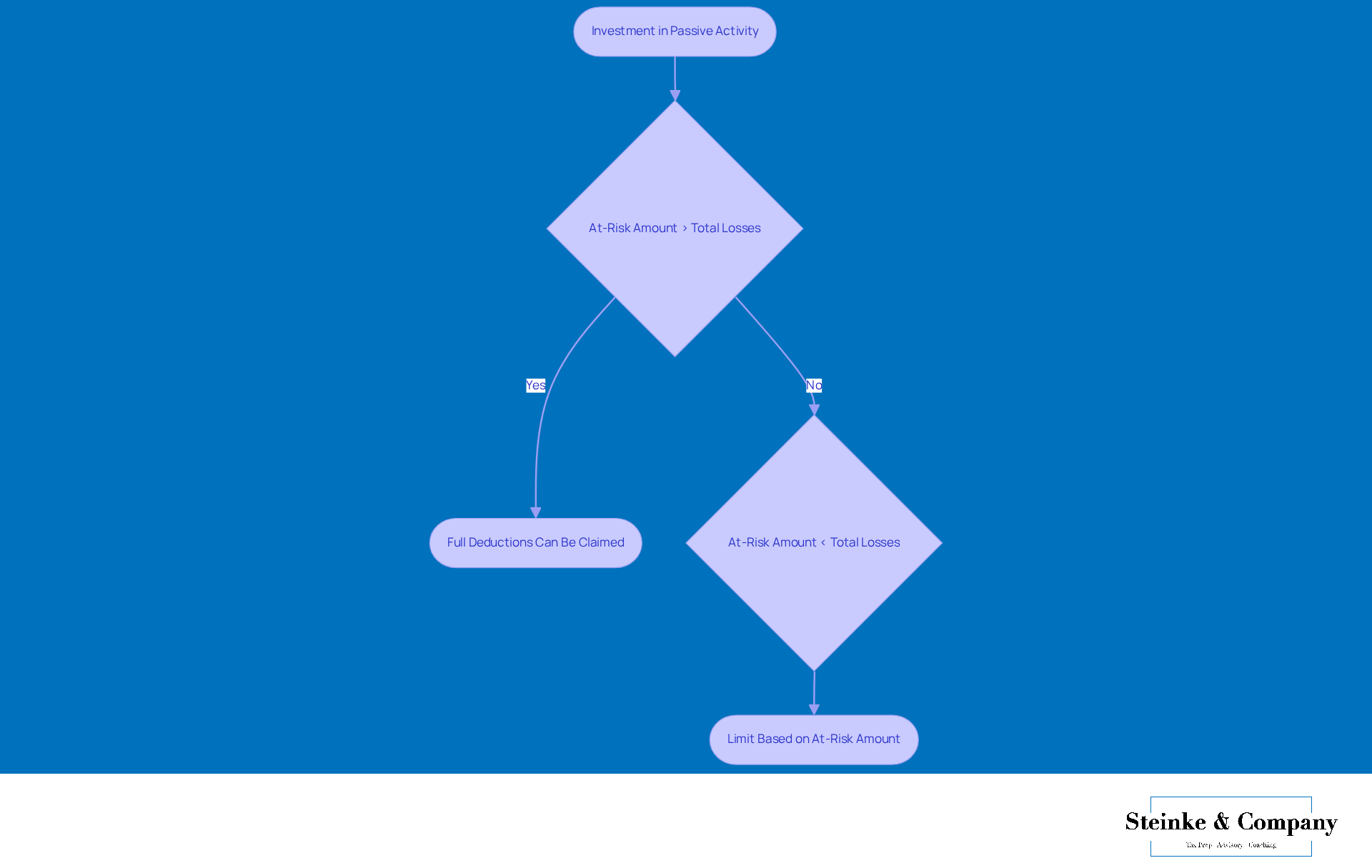
The at-risk rule is super important when it comes to figuring out if you can deduct those inactive expenses. Essentially, it limits your deductions to the amount you’ve got at risk in the activity. Let’s say your investment in a passive activity takes a nosedive and drops below zero. In that case, you can’t claim deductions that go beyond your at-risk amount. This limitation, known as the passive activity loss limitation, really hits home for small business owners because it directly affects how they can claim deductions and manage their tax responsibilities.
Imagine a small business owner who puts $50,000 into a rental property but then faces some setbacks that lower their at-risk amount to $30,000. According to the at-risk rule, they can only deduct losses up to $30,000, even if their total losses are higher. This example really highlights why it’s crucial to understand these at-risk limitations; they can have a major impact on cash flow and tax planning strategies.
Tax pros often stress the importance of keeping meticulous records and staying aware of your at-risk amounts. One expert put it nicely: 'Navigating the at-risk limitations requires a clear understanding of your investments and the associated risks. Without this knowledge, small business owners may miss out on valuable deductions.'
But wait, there’s more! The effects of at-risk limitations go beyond just immediate deductions. For small businesses, the passive activity loss limitation can make it tricky to offset unused deductions against other income, which complicates overall tax strategies. For instance, if a small business owner has multiple inactive activities, they need to file Form 6198 for each one. This ensures that their losses are properly tracked and documented.
In a nutshell, the at-risk rule is a key player for small business owners looking to maximize their tax deductions. By being aware of these limitations and seeking professional advice, they can better navigate the complexities of inactive expense deductions and ultimately improve their financial outcomes.
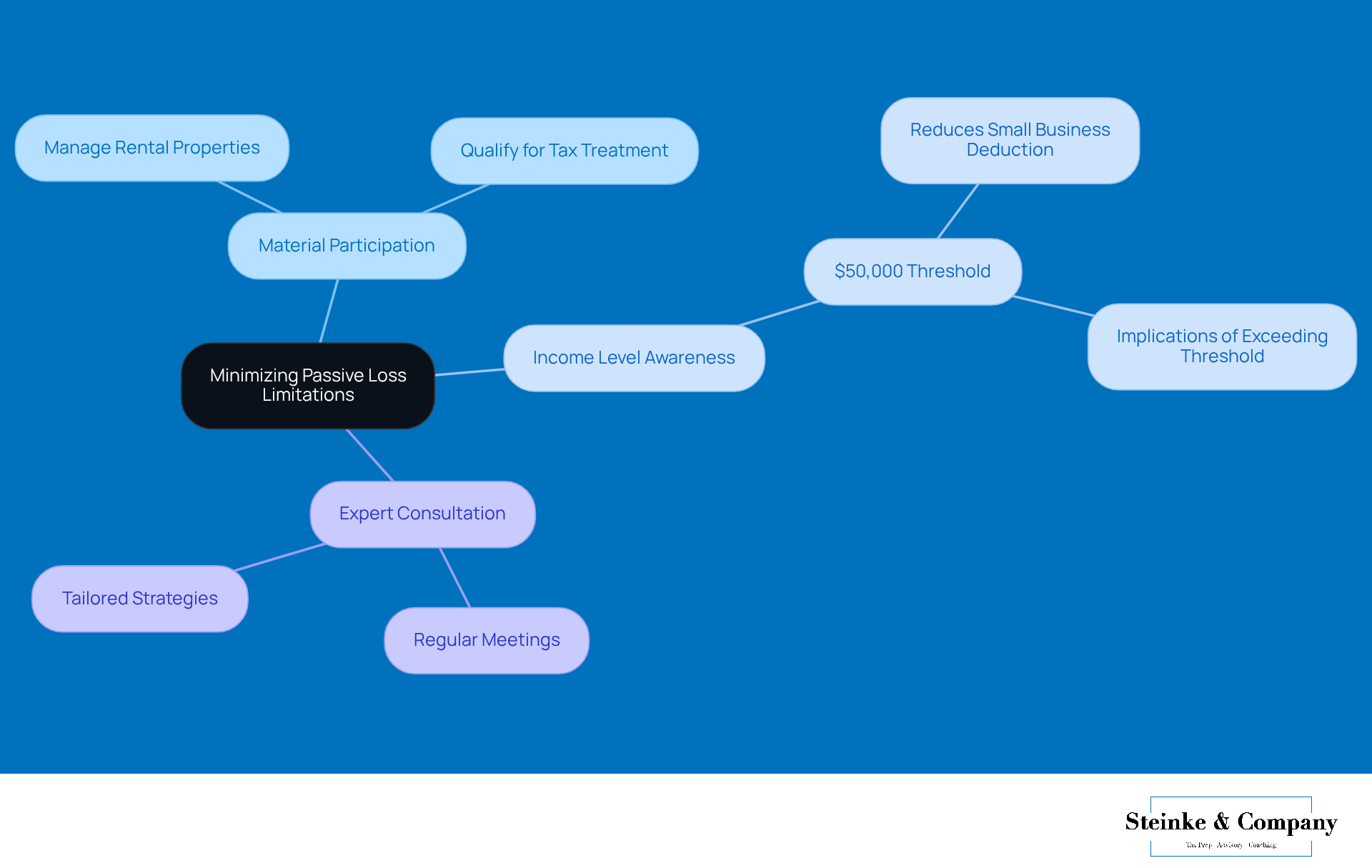
Minimizing Passive Loss Limitations: Legal Strategies for Taxpayers
If you're a small business owner looking to cut down on passive activity loss limitation, there are some smart strategies you can implement. One effective approach is to reorganize your activities to ensure you’re materially participating in your business. This can help you qualify for better tax treatment. For example, if you actively manage rental properties, you can take advantage of the special allowance for rental real estate, which lets you offset up to $25,000 in losses against non-passive income—just make sure you meet the necessary criteria!
Keeping an eye on your income levels is also super important. You’ll want to stay under the $50,000 mark in investment earnings because going over that can reduce your small business deduction by $5 for every extra dollar you earn. This really highlights the need for proactive tax planning, especially with all the recent changes in tax benefits following the end of COVID-19 relief measures. Many small business owners are now facing smaller tax refunds and need to navigate these new complexities.
Tax consultants often suggest that regular meetings can lead to tailored strategies that not only tackle those pesky inactive setbacks but also boost your overall financial health. For instance, Steinke and Company provides tax planning services that include regular check-ins and strategic planning sessions designed just for your goals. Some savvy small business owners have successfully reorganized their operations to ensure they’re actively involved, maximizing their tax benefits in the process. By putting these strategies into action and tapping into expert advice, you can better manage the passive activity loss limitation and really optimize your tax outcomes.
So, what steps will you take to enhance your tax strategy?
Conclusion
Understanding passive activity loss limitations is super important for small businesses looking to optimize their tax strategies. This article breaks down the key components of these limitations and what they mean for you, highlighting why informed tax planning and compliance are essential. By getting a handle on passive activity losses, small business owners can navigate their tax obligations more effectively and even lower their overall tax burden.
So, what should you keep in mind? First off, maintaining accurate records is crucial. Also, be sure to familiarize yourself with IRS Form 8582 for reporting losses. And don’t forget about material participation—it plays a big role in claiming those deductions! There are also some exceptions, like the special allowance for rental real estate and the at-risk rule, which can help you maximize your tax benefits. With a proactive approach and some expert guidance, you can manage your passive activity losses and make the most of available deductions.
Ultimately, we encourage small business owners to take charge of their tax situations by staying informed and considering professional tax compliance services. By putting these strategies into action, you can boost your financial health and avoid leaving potential savings on the table. Remember, the tax landscape is always changing, so it’s crucial to stay vigilant and adaptable in your quest for effective tax management.
Frequently Asked Questions
What services does Steinke and Company offer for small businesses?
Steinke and Company provides tailored tax compliance solutions, focusing on understanding and managing passive activity loss limitations. They offer proactive tax planning services to help businesses navigate tax complexities and select appropriate accounting methods.
Why is it important for small businesses to understand passive activity loss limitations?
Understanding passive activity loss limitations is crucial for service-oriented businesses as it directly impacts tax reporting and deductions. Proper knowledge can help businesses manage their tax obligations and minimize their overall tax liability.
What are the recent changes to the 1099-K reporting requirements?
The recent updates to the 1099-K reporting requirements stipulate that transactions over $600 need to be reported, making it essential for small businesses and gig economy taxpayers to maintain accurate records of their income and expenses.
What is IRS Form 8582, and why is it important?
IRS Form 8582 is used to report passive activity losses. It helps taxpayers determine how much non-operating deductions they can claim under the passive activity loss limitation, making it crucial for maximizing deductions and avoiding penalties.
What is material participation, and how does it affect passive loss deductions?
Material participation refers to the level of engagement a taxpayer has in an economic activity, typically requiring over 500 hours of involvement in a year. It is important for qualifying for non-active deduction benefits, as it impacts the ability to write off losses from non-active ventures.
How can keeping detailed records benefit small business owners regarding tax deductions?
Maintaining accurate records can substantiate claims of material participation, which is critical for offsetting inactive losses against other income. This practice can significantly influence a small business owner's overall tax situation and help reduce tax bills.