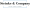Overview
Let’s break it down: the article dives into the difference between profit and revenue, and why it matters for understanding a business's financial health. So, what’s the scoop? Revenue is basically the total cash coming in from sales before any expenses are taken out. On the flip side, profit is what’s left after all those pesky costs are accounted for. This distinction isn’t just some financial jargon; it’s super important for managing your finances effectively and planning strategically for the future.
Think about it: if you’re running a business, knowing how much money is coming in versus what you actually get to keep can make all the difference. It’s like knowing the difference between your paycheck and what you can actually spend after bills. So, next time you’re looking at your financials, remember this key difference—it could really help steer your business in the right direction!
Introduction
Understanding the financial landscape of a business isn’t just about taking a quick look at the income statement; it’s about really grasping the difference between revenue and profit. Think of revenue as the 'top line'—it’s the total income you bring in from sales. Profit, on the other hand, is the 'bottom line'—it shows what’s left after all your expenses are taken out. This distinction is crucial because it not only gives business owners a snapshot of their financial health but also influences their strategic decisions.
But here’s the kicker: how do you navigate the tricky waters of financial management when high revenue doesn’t always mean you’re making a profit? It’s a question worth pondering, and exploring it can lead to some valuable insights for sustainable growth and smart cost management. So, let’s dive in and unravel this together!
Define Revenue and Profit
Revenue is basically the total income you make from selling goods or services before any deductions. You might hear it called the 'top line' on an income statement. On the flip side, profit is what’s left after you’ve taken out all your costs, taxes, and fees—often referred to as the 'bottom line.' Understanding the profit and revenue difference is crucial for gauging how well your business is doing and for making smart decisions.
- Revenue: Total income from sales.
- Profit: Income left after costs.
For instance, let’s say a small business rakes in $100,000 in sales but spends $70,000 on costs. That leaves a profit of $30,000. Understanding the profit and revenue difference is key for effective financial management, as it helps business owners evaluate their performance and plan for growth.
Now, when it comes to tracking income and expenses, there are a few accounting methods to think about. The cash method records income when you actually receive payment, which can make cash flow management a breeze for small business owners. On the other hand, the accrual method logs revenue when a sale happens, giving you a clearer picture of your financial health, but it does require careful management of accounts receivable. Then there’s hybrid accounting, which combines both methods. This is especially handy for businesses that keep inventory, as it allows for monitoring cash flow while managing inventory on an accrual basis.
When you’re picking the right accounting method, consider things like the size of your business, your growth plans, and whether you have investors involved. Taking the time to think this through will help ensure that the method you choose aligns with your financial goals.
Identify Key Differences Between Revenue and Profit
Let’s break down the key differences between revenue and profit in a way that’s easy to digest:
-
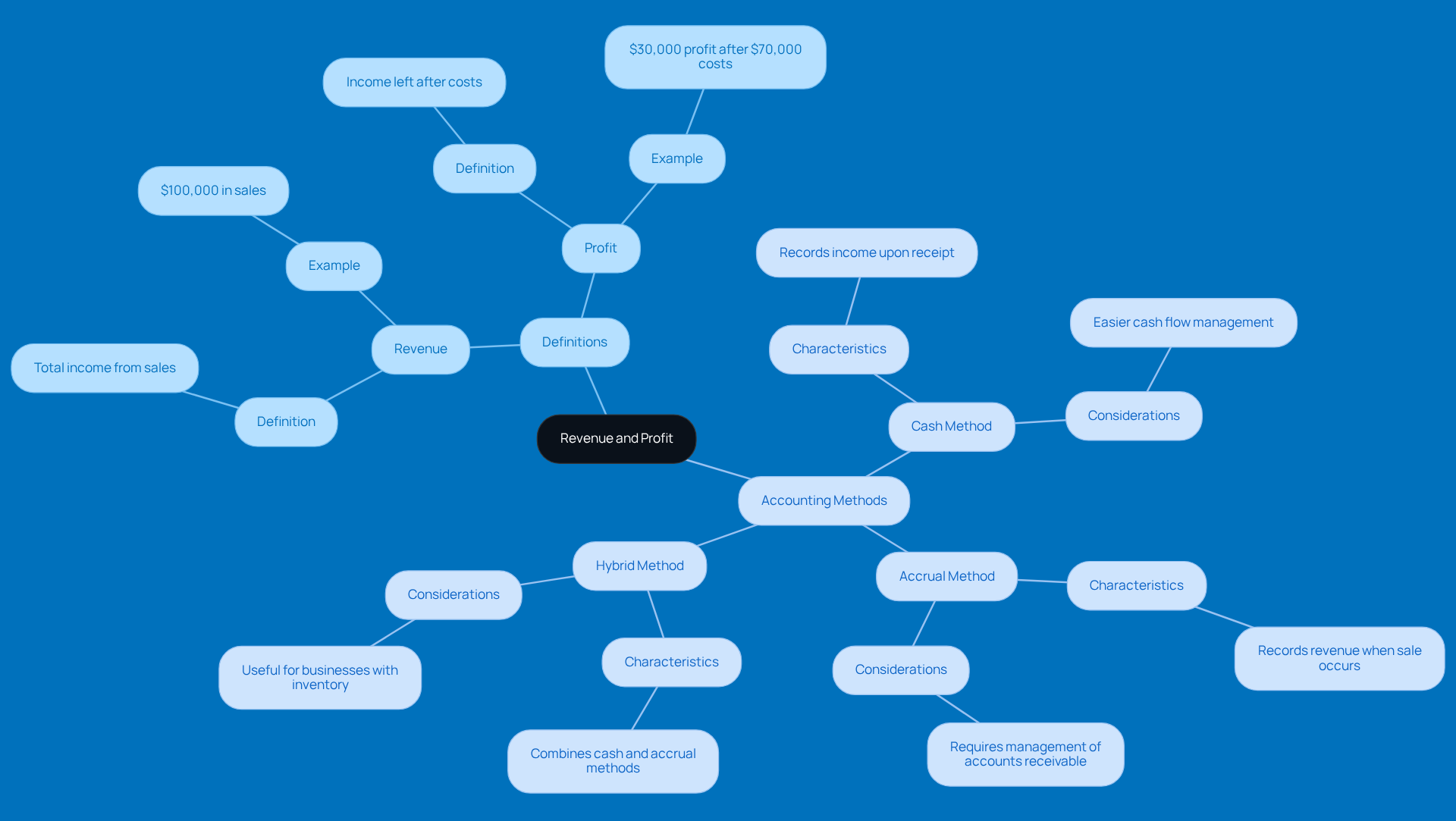
Measurement: Think of revenue as the total income a business rakes in from sales before any costs come into play. Profit, on the other hand, is what’s left after all expenses—like operating costs, taxes, and interest—are taken into account.
-
Implications: Just because a company has high revenue doesn’t mean it’s making a profit. Picture this: a business might report $500,000 in income but have costs that hit $600,000. That’s a $100,000 loss! This really highlights how crucial it is to manage costs effectively, especially when companies are trying to grow from $1 million to $10 million in revenue. Finding that sweet spot between bringing in money and keeping expenses in check is key to sustainable growth.
-
Financial Statements: Revenue shows up at the top of the income statement—often called the 'top line'—while profit is found at the bottom, known as the 'bottom line.' This distinction is super important for understanding a company’s financial health. It tells you how much cash is left after all the bills are paid.
Understanding the profit and revenue difference is vital for small businesses, particularly for those that may experience impressive income yet struggle with profitability. Financial experts often point out that while growing income can indicate market demand and business expansion, it’s the profit that keeps the lights on and allows for reinvestment. As companies move along their growth journey, they also need to think about their risk tolerance and marketing strategies to ensure they’re not just making money but also managing expenses wisely.
So, how can businesses tackle cost management? Regularly reviewing expenses, sticking to budgets, and finding efficiencies in operations are all great strategies. There are plenty of real-world examples out there—many businesses boast impressive income figures yet face challenges due to high operational costs. This really underscores the importance of balancing income generation with smart cost management.
What’s your experience with managing costs in your business? It’s a tricky balance, but with the right strategies, it can definitely be done!
Calculate Revenue and Profit Accurately
To accurately calculate revenue and profit, let’s break it down into some essential steps:
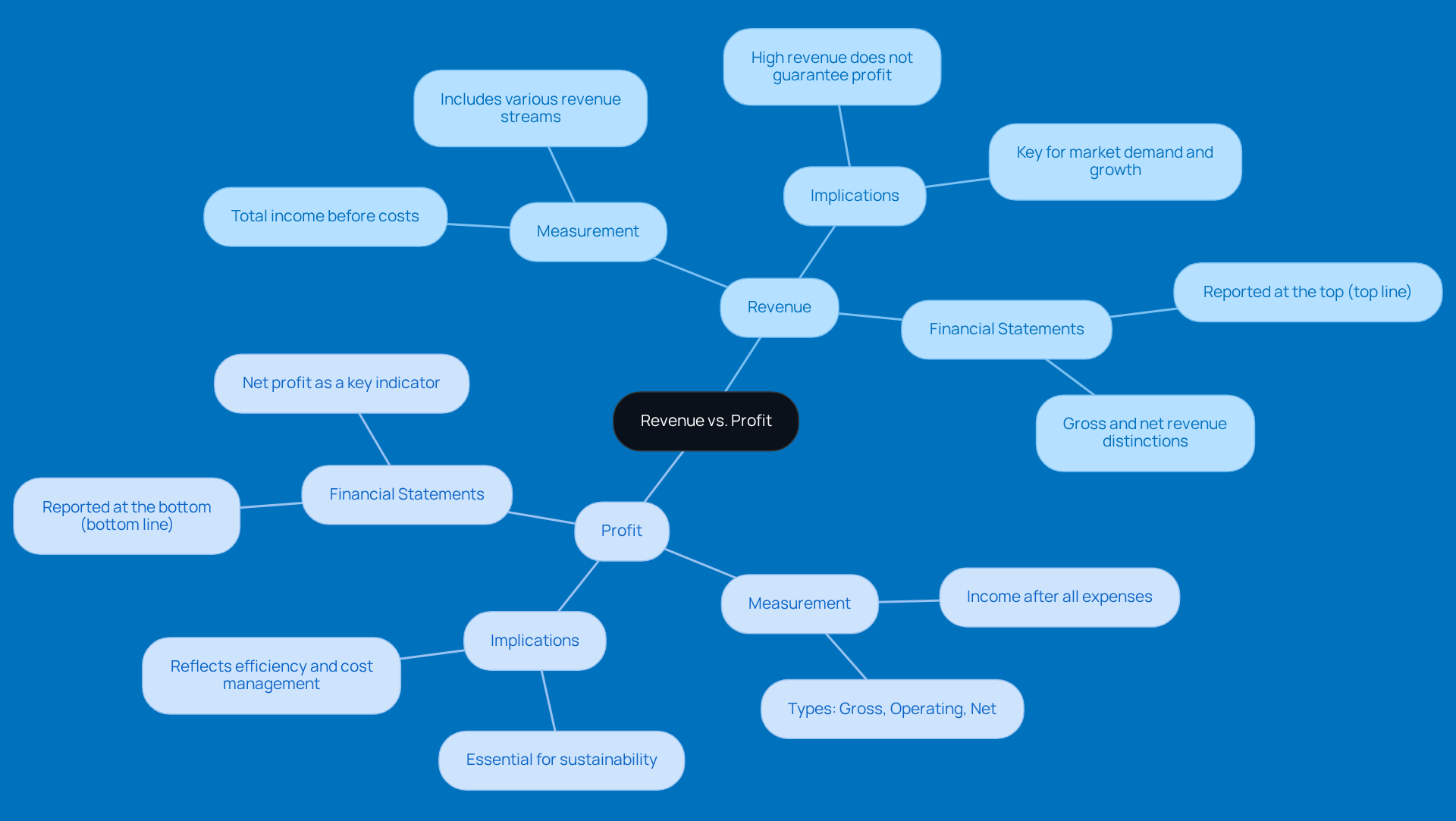
Step 1: Calculate Revenue
- Formula: Revenue = Price per Unit × Number of Units Sold
- Example: If you sell a product for $50 and move 1,000 units, your revenue totals a neat $50,000. Not too shabby, right?
Step 2: Calculate Total Expenses
- Include: Cost of goods sold (COGS), operating expenses, taxes, and any additional costs.
- Example: If your total expenses come to $30,000, that figure covers all the costs tied to running your business.
Step 3: Calculate Profit
- Formula: Profit = Revenue - Total Expenses
- Example: Using our earlier numbers, Profit = $50,000 - $30,000 = $20,000. Easy peasy!
Understanding Accounting Methods
Now, when you’re calculating revenue and profit, it’s super important to think about the accounting method your business uses. The cash method records income when payment is received, which can make cash flow management a breeze for smaller businesses. On the flip side, the accrual method recognizes revenue when a sale happens, giving you a clearer picture of your financial health but requiring you to keep a close eye on accounts receivable. Then there’s hybrid accounting, which blends both methods, helping you manage cash flow while keeping tabs on inventory. Picking the right accounting approach can really shape your financial clarity and decision-making.
Best Practices for Calculation
Make it a habit to document and review all your calculations regularly. This helps ensure accuracy and keeps you in line with tax regulations. Plus, it can save you from common pitfalls, like miscalculating expenses or overlooking variable costs, which can really impact your profit margins. As financial author Marshall Hargrave puts it, 'Using the earnings formula to evaluate your company is something every owner should do consistently—at least monthly.'
Final Note
Understanding the difference between revenue and profit is key for long-term sustainability. While income shows your commercial activity, the profit and revenue difference reflects your financial health and your ability to reinvest in your business. Did you know the typical yearly income for small businesses is around $1,221,884? That’s a lot of potential for growth! By following these steps and keeping thorough records, you can boost your financial clarity and make informed choices for your rural enterprise.
Apply Revenue and Profit Insights to Business Strategy
To really make the most of your understanding of revenue and profit, let’s weave these insights into your business strategy:
-
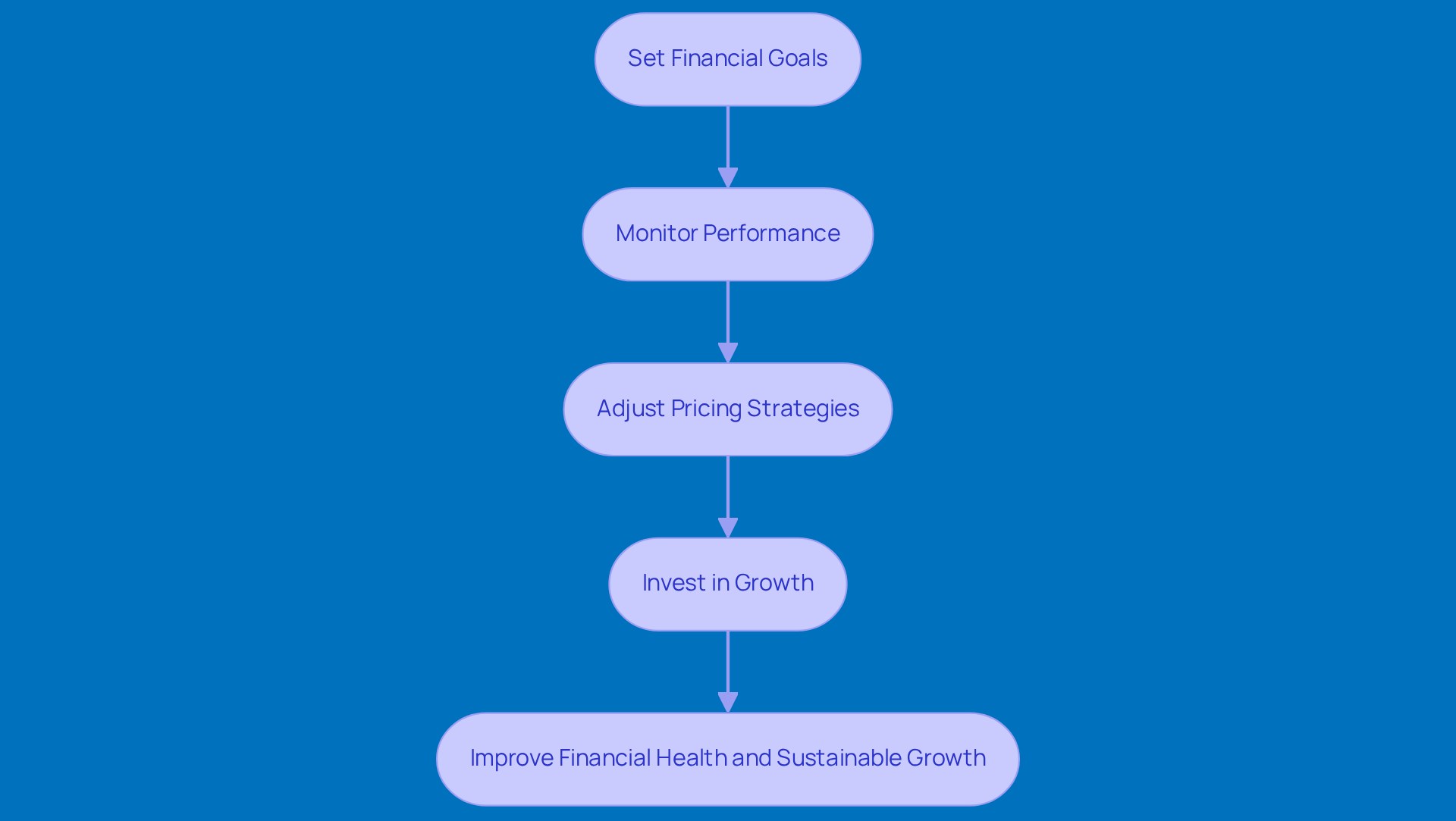
Set Financial Goals
Think about using your revenue and profit data to set some realistic financial targets that can help you grow. For instance, a small business might aim for a 15% increase in net earnings over the next six months. It’s all about aligning your efforts with clear goals that you can actually achieve. -
Monitor Performance
Keep an eye on your revenue and profit margins regularly. This way, you can spot trends and find areas that need a little TLC. Ongoing evaluations can provide you with valuable insights into the profit and revenue difference, determining whether your pricing strategy aligns with market demand and operational costs. -
Adjust Pricing Strategies
If you notice that your profit margins are looking a bit sad, it might be time to rethink your pricing structure or look into ways to cut costs. For example, a cleaning service could compare its pricing with competitors to ensure it stays competitive while still making a profit. -
Invest in Growth
Why not reinvest those profits back into your business? This can really kickstart growth initiatives, like ramping up your marketing efforts, developing new products, or boosting operational efficiencies. If you’ve got a stable profit margin of 20%, consider allocating some of those profits to expand your product line. It’s a great way to increase both revenue and market share.
By putting these strategies into action, small businesses can not only improve their financial health but also set themselves up for sustainable growth in a competitive landscape. So, what are you waiting for? Let’s get started!
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between revenue and profit is super important for any business looking to grow and thrive. Think of revenue as the total cash coming in from sales, while profit shows how well a business is really doing after all the bills are paid. This key distinction is vital for making smart decisions that can shape the future of your enterprise.
In this article, we’ve explored the ins and outs of revenue and profit, covering their definitions, how to measure them, and what each means for your business performance. We’ve also talked about the importance of picking the right accounting method—whether it’s cash, accrual, or a mix of both—to get a true picture of your financial health. Plus, we’ve shared some practical steps for calculating revenue and profit, so you can keep a clear view of where your business stands financially.
Ultimately, using insights from your revenue and profit calculations can really help steer your business decisions. Setting financial goals, keeping an eye on performance, tweaking pricing strategies, and reinvesting profits are all crucial steps that can lead to sustainable growth. By understanding the importance of both revenue and profit, you can navigate your financial landscape more effectively and set the stage for long-term success. So, what’s your next move? Let’s keep the conversation going!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is revenue?
Revenue is the total income generated from selling goods or services before any deductions. It is often referred to as the 'top line' on an income statement.
What is profit?
Profit is the income that remains after all costs, taxes, and fees have been deducted from revenue. It is commonly called the 'bottom line.'
Why is it important to understand the difference between revenue and profit?
Understanding the difference between revenue and profit is crucial for assessing business performance and making informed financial decisions.
Can you provide an example of revenue and profit?
For instance, if a small business generates $100,000 in sales and incurs $70,000 in costs, the profit would be $30,000.
What are the different accounting methods for tracking income and expenses?
The main accounting methods include:
- Cash method: Records income when payment is received, simplifying cash flow management.
- Accrual method: Records revenue when a sale occurs, providing a clearer picture of financial health but requiring careful management of accounts receivable.
- Hybrid accounting: Combines both methods, useful for businesses with inventory as it allows monitoring cash flow while managing inventory on an accrual basis.
What factors should be considered when choosing an accounting method?
When selecting an accounting method, consider the size of your business, growth plans, and whether there are investors involved. This ensures the chosen method aligns with your financial goals.