Introduction
Understanding tax obligations can feel like a maze, especially for small business owners. Take Schedule K-1, for instance. This important tax document not only breaks down each partner's share of earnings but also plays a big role in figuring out tax liabilities and compliance. As the world of small business taxation changes, tackling the ins and outs of K-1 distributions can seem overwhelming. So, how can you manage your K-1 tax responsibilities effectively while also maximizing your financial outcomes? Let's dive in!
Define Schedule K-1 and Its Importance for Small Businesses
Schedule K-1 is a key tax document that you’ll want to get familiar with if you’re involved in a partnership or an S corporation. It reports earnings, deductions, and credits, and each partner or shareholder gets their own K-1 that outlines their share of the entity's earnings. This is important because you need to report this information on your personal tax returns.
For small business owners, understanding K-1 is crucial. Why? Because it directly impacts your tax liabilities and compliance. Getting the reporting right on your K-1 can help you avoid penalties and ensure that all your earnings are documented properly. This is especially vital for small businesses that might not have a full accounting team at their disposal.
Take a moment to carefully review each line item on your K-1. By doing so, you can maximize your deductions and credits, which can really boost your financial outcomes. So, next time you receive your K-1, don’t just file it away - take a closer look and see how it can work in your favor!
Explore Tax Implications of K-1 Distributions
K-1 payments come with some important implications related to the K-1 distribution tax rate for small business owners, and it’s worth diving into! Unlike your typical earnings, K-1 payments usually aren’t subject to self-employment tax, which can lead to some pretty significant savings. Generally, it’s the general partners who are on the hook for self-employment tax on their distributive shares of earnings, while limited partners get to sidestep this tax on their K-1 distributions. But don’t forget, the earnings reported on a K-1 are still taxable at the K-1 distribution tax rate.
Let’s say a partnership rakes in $100,000 in taxable income. If you own 50% of that business, your K-1 might show a share of $50,000. If you take out more than your basis in the partnership, you could end up facing capital gains tax, which adds another layer of complexity to your tax planning. In 2021 alone, over 4 million returns were filed involving more than 30.6 million partners, showing just how common K-1s are in the world of small business taxation.
Experts really stress the importance of understanding these nuances related to the K-1 distribution tax rate. They recommend that business owners keep a close eye on their K-1 allocations and related tax obligations to avoid any nasty surprises come tax time. For instance, if a partnership recorded a loss of $40,000 in its first couple of years, the tax implications could shift dramatically as it starts turning a profit. Staying informed about your tax responsibilities is key!
Navigating K-1 tax liabilities can feel a bit daunting, but with the right planning and resources, small business owners can manage their tax responsibilities effectively and enjoy the perks that come with K-1 allocations. So, are you ready to tackle those K-1s?
Calculate Your K-1 Distribution Tax Rate
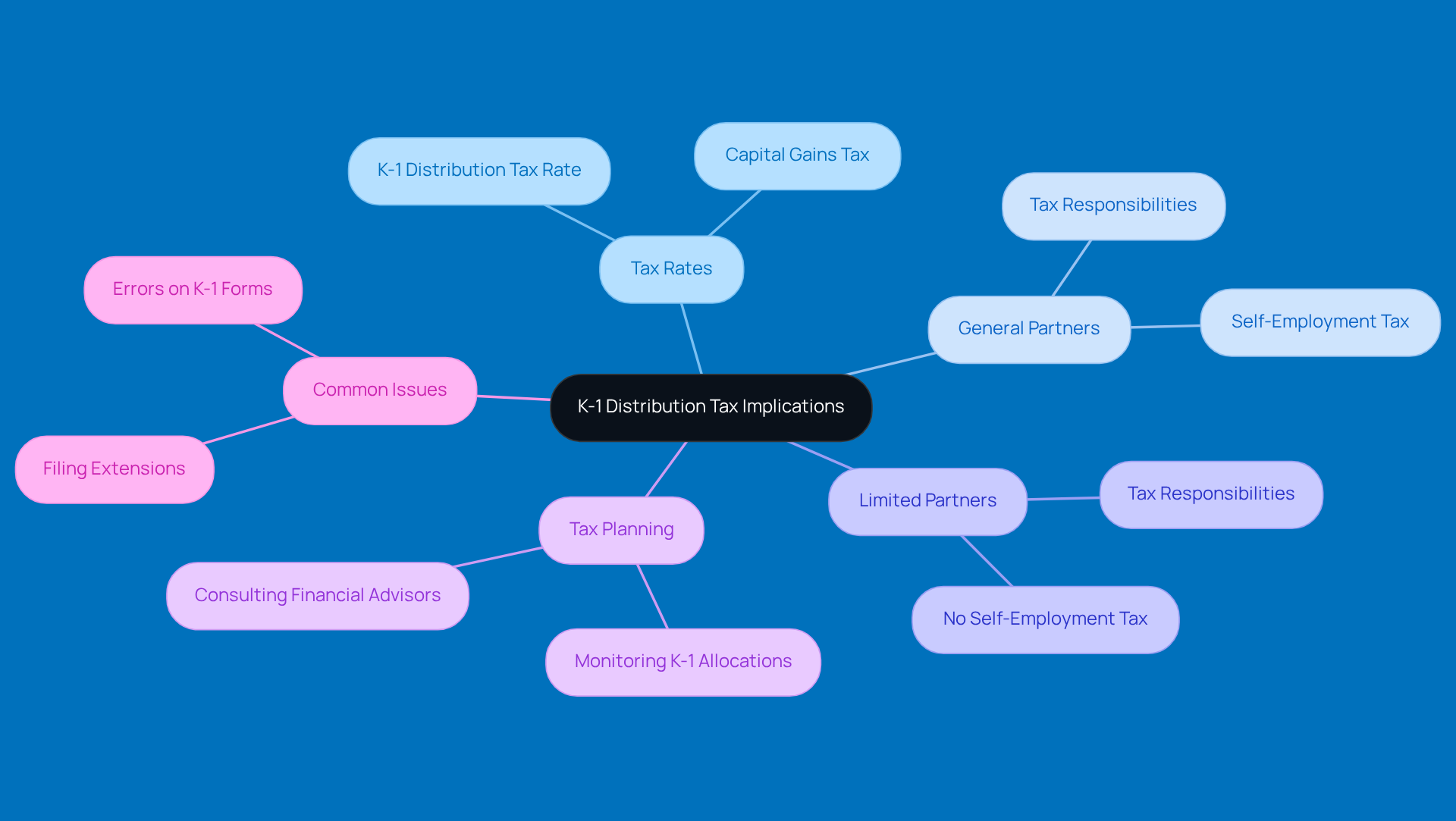
Determining your K-1 distribution tax rate is simpler than you may believe! Let’s break it down into a few simple steps.
- First, you’ll want to identify the total earnings reported on your K-1.
- Next, figure out your tax bracket based on your total taxable earnings, which includes that K-1 revenue.
- Finally, apply the right tax rate to your K-1 earnings.
For instance, if your K-1 shows $10,000 in earnings and your total taxable income puts you in the 22% tax bracket, your tax obligation from the K-1 would be $2,200. Pretty straightforward, right? This calculation is super important for understanding your overall tax burden and planning for those payments down the line.
Looking ahead to 2026, the tax brackets for individuals are set up progressively, with rates ranging from 10% to 37%, depending on how much you earn. Familiarizing yourself with these brackets can really help you make informed decisions about your K-1 earnings and the K-1 distribution tax rate in your overall tax strategy. So, what do you think? Are you ready to tackle your K-1 like a pro?
Implement Strategies to Optimize K-1 Tax Outcomes
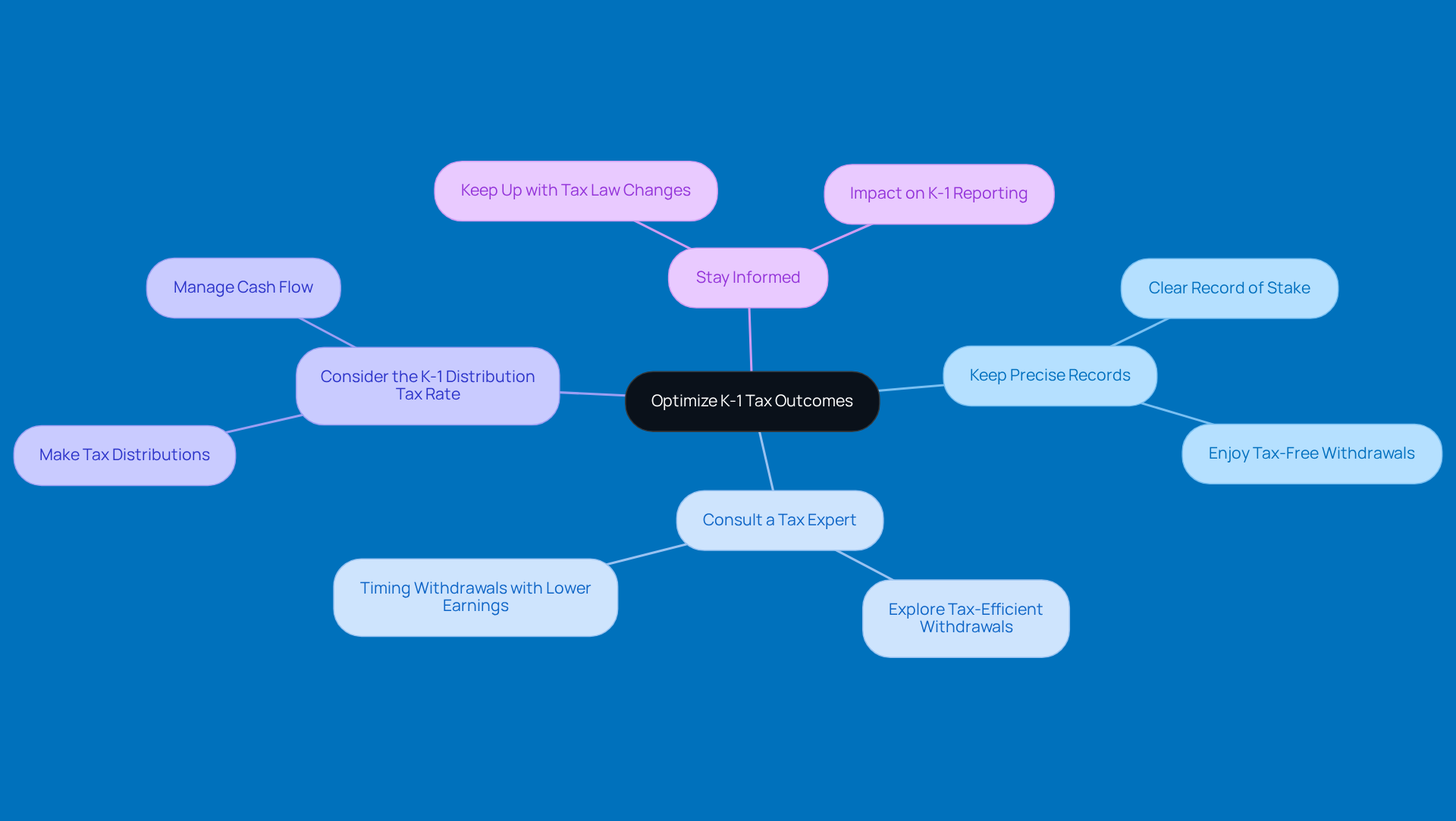
Do you want to optimize your K-1 distribution tax rate outcomes? Here are some friendly strategies to consider:
-
Keep Precise Records: Make sure you have a clear record of your stake in the partnership. This way, you can fully enjoy those tax-free withdrawals!
-
Consult a Tax Expert: It’s always a good idea to chat with a tax pro. They can help you explore alternatives for tax-efficient withdrawals, like timing them with years when your earnings are lower.
-
Consider the K-1 distribution tax rate: Think about making tax distributions to cover the tax liability on your K-1 income. This can really help with managing your cash flow.
-
Stay Informed: Tax laws change, and it’s important to keep up with any updates that might affect your K-1 reporting and taxation.
By implementing these strategies, you can effectively manage your tax liabilities and boost your business's financial stability. So, what do you think? Ready to take charge of your K-1 taxes?
Conclusion
Understanding Schedule K-1 and its tax implications is super important for small business owners. This document not only shows each partner's share of earnings but also helps determine tax liabilities. By getting a handle on K-1 distributions, you can tackle your tax responsibilities more effectively, leading to better financial outcomes.
Throughout this article, we’ve highlighted some key points. We talked about the importance of accurately reporting K-1 earnings, how you can save by avoiding self-employment tax, and the simple steps to calculate the K-1 distribution tax rate. Plus, we shared strategies like keeping precise records, consulting tax pros, and staying updated on tax law changes to help you optimize your tax outcomes.
So, let’s wrap this up! The impact of K-1 distributions on small business taxes is huge. By taking proactive steps to understand and manage K-1 reporting and tax obligations, you can not only reduce potential liabilities but also boost your overall financial health. Embracing these practices will empower you to take charge of your tax strategies and secure a more stable financial future. Ready to take the next step?
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Schedule K-1?
Schedule K-1 is a tax document used by partnerships and S corporations to report earnings, deductions, and credits. Each partner or shareholder receives their own K-1 that details their share of the entity's earnings.
Why is Schedule K-1 important for small businesses?
Schedule K-1 is important for small businesses because it directly affects tax liabilities and compliance. Proper reporting on the K-1 helps avoid penalties and ensures that all earnings are accurately documented.
How does Schedule K-1 impact personal tax returns?
The information reported on Schedule K-1 must be included in the individual partners' or shareholders' personal tax returns, impacting their overall tax obligations.
What should small business owners do with their K-1?
Small business owners should carefully review each line item on their K-1 to maximize deductions and credits, which can enhance their financial outcomes.
What can happen if K-1 reporting is not done correctly?
Incorrect reporting on Schedule K-1 can lead to penalties and issues with tax compliance, making it essential for small businesses to ensure accurate documentation.