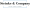Introduction
Understanding the ins and outs of Qualified Business Income (QBI) can really make a difference for rental property owners. This important tax provision lets landlords potentially deduct up to 20% of their qualified business income from taxable earnings, which can lead to some serious savings. But let’s be honest - figuring out the eligibility criteria and how to calculate it can feel overwhelming. What exactly counts as business income in the eyes of the IRS?
So, what steps should landlords take to make the most of their QBI benefits while steering clear of common pitfalls? Let’s dive in and explore!
Understand Qualified Business Income and Its Importance for Rental Properties
Qualified Business Income (QBI) is all about the net earnings you make from a qualified trade or business. This can even include leased properties under certain conditions! Understanding qualified business income rental property is super important for property owners because it might allow you to deduct up to 20% of your qualified business income rental property from your taxable income, which can really help lower your tax bill. This tax break is especially great for small business owners and property owners, as it can lead to some serious savings.
Now, to qualify for this deduction, your leasing activity needs to be recognized as a trade or business related to qualified business income rental property. That usually means you have to be regularly and continuously involved in the leasing operations. For instance, if you want to be recognized as a real estate professional, you need to spend more than half of your total working hours on real estate businesses, with at least 750 hours each year. Plus, keep in mind that the QBI deduction is available for tax years starting after December 31, 2017, and ending on or before December 31, 2025.
Getting to know the ins and outs of QBI can really help you make smart choices that boost your property's profitability and tax efficiency. Just a heads up: owning two qualified business income rental properties, each requiring 125 hours of eligible leasing services per year, won’t meet the 250-hour test needed to qualify. Understanding these details can help landlords like you maximize those tax benefits!
Determine Eligibility: Does Your Rental Income Qualify as Business Income?
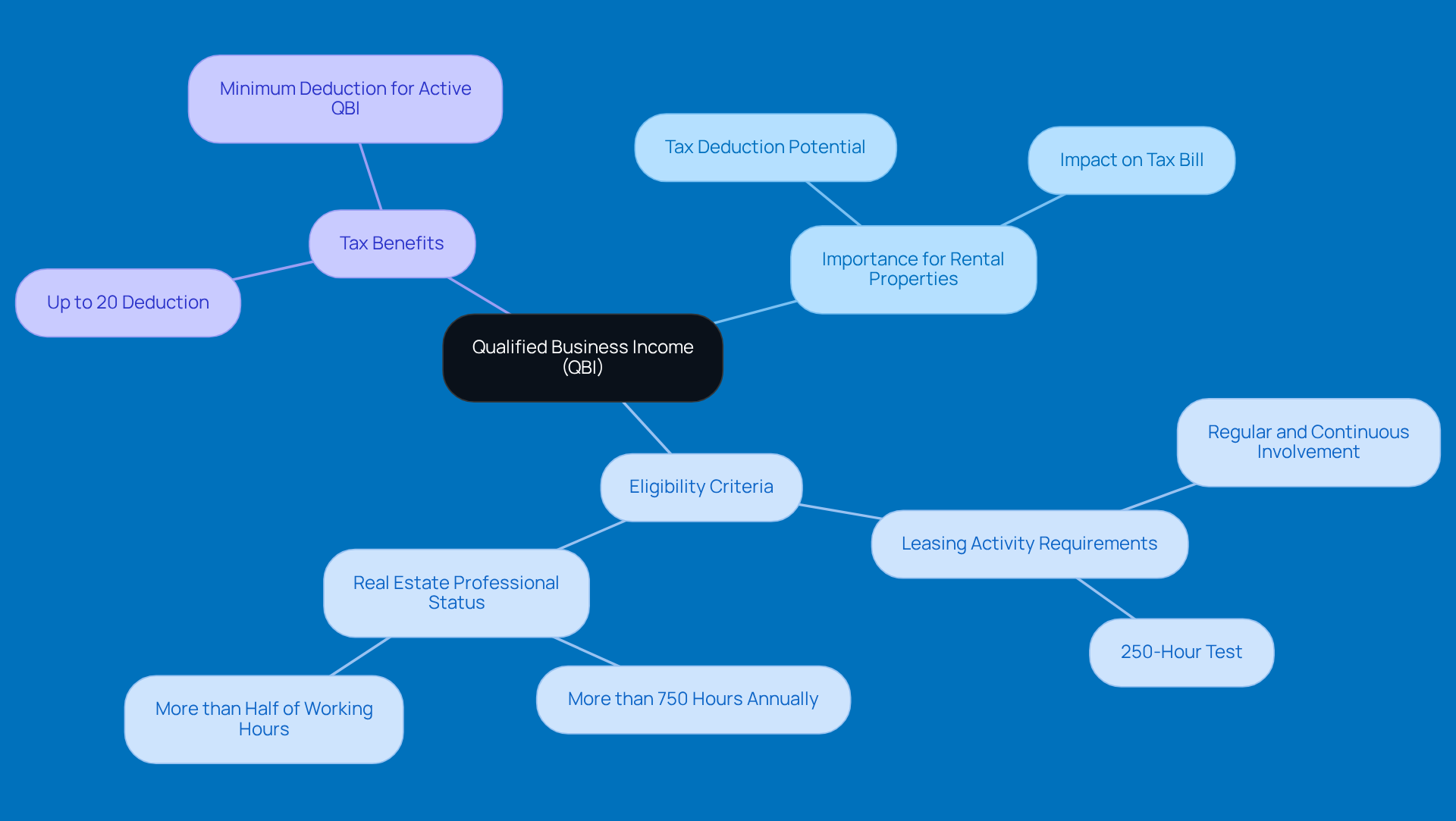
If you're wondering whether your income from leasing counts as qualified business income rental property, you’ll want to check if your leasing activities meet the IRS's trade or business criteria. This boils down to showing that you’re actively involved in managing the property. Here are some key points to consider:
- Regular and Continuous Activity: You need to be hands-on with your property management. This usually means putting in a good chunk of time on leasing tasks - think tenant communication, property upkeep, and keeping an eye on finances.
- Separate Books and Records: Keeping your financial records separate for your leasing activities is a must. This helps you clearly distinguish between your business earnings and personal income, which is crucial for compliance and can save you during audits.
- Safe Harbor Requirements: The IRS has a safe harbor for rental real estate businesses, which says landlords should provide at least 250 hours of rental services each year. Hitting this mark not only boosts your chances of qualifying for qualified business income rental property but also simplifies the entire process.
Also, don’t forget about the revenue limits for QBI reductions. For 2024, these are set at $191,950 for individual filers and $383,900 for joint filers. By 2026, there’ll be a minimum $400 QBI allowance for those with at least $1,000 of active QBI. Just a heads up, some types of leasing income, such as income from qualified business income rental property or triple-net leases, aren’t included in QBI.
By taking a close look at these factors and keeping your records up to date for at least three years (seven years is even better for peace of mind), you can figure out if you’re eligible for the QBI benefit. Plus, many property owners successfully meet these standards by tracking their hours and maintaining detailed records, which can really boost their chances of snagging that tax benefit in 2026. So, why not start organizing your records today?
Calculate Your QBI Deduction for Rental Properties
Calculating your Qualified Business Income (QBI) deduction might sound a bit daunting, but it’s really just a few straightforward steps. Let’s break it down together:
-
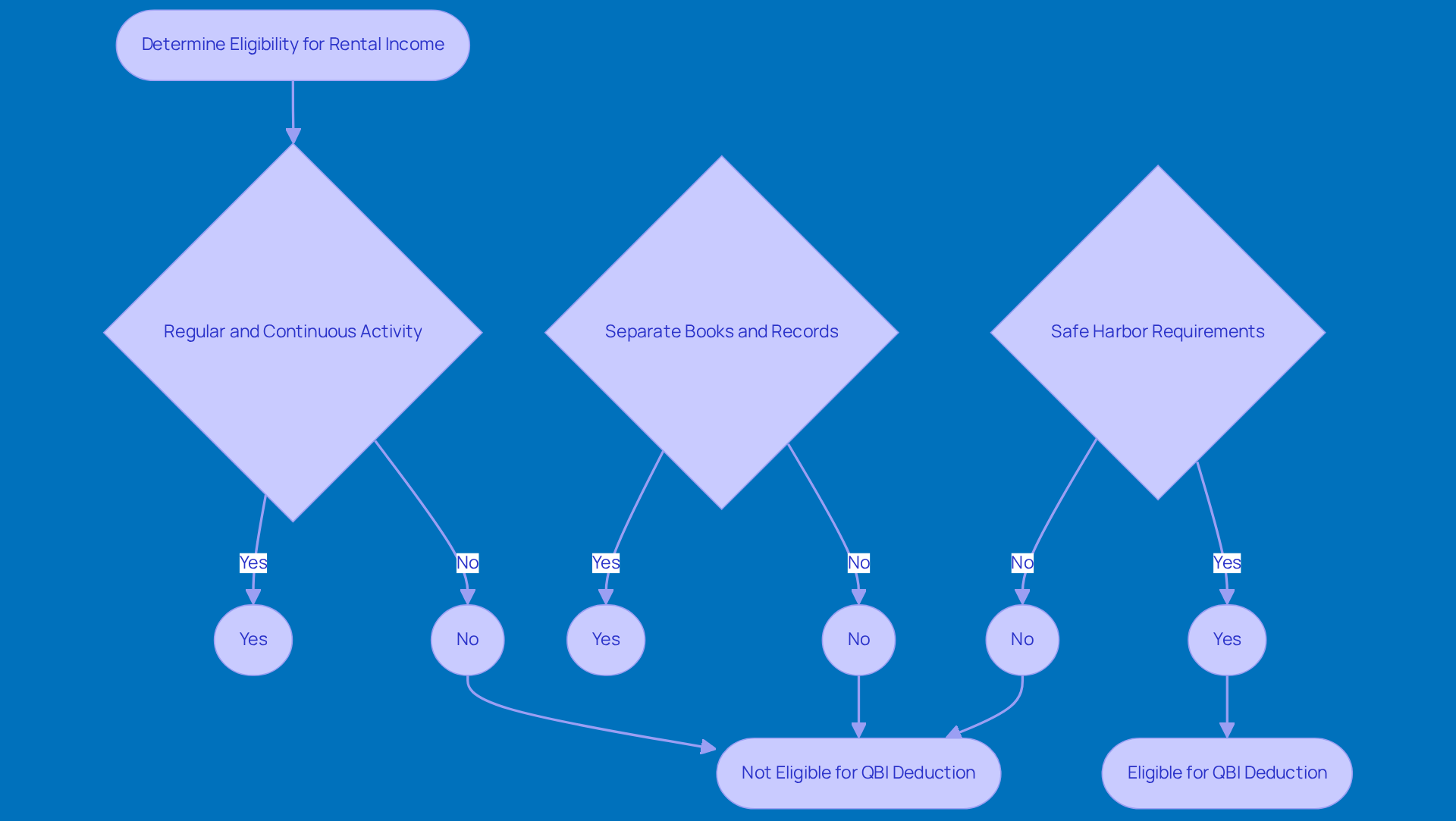
Calculate Your Net Lease Earnings: First things first, you’ll want to figure out your total lease earnings. Don’t forget to deduct any allowable expenses related to the property - think maintenance, repairs, and property management fees. This gives you a clear picture of your net earnings from leasing.
-
Identify your qualified business income rental property: Your qualified business income rental property is essentially the net rental revenue that qualifies after those expenses are taken out. Just ensure that this revenue is generated from a qualified business income rental property, as defined by the IRS.
-
Calculate the Reduction: Here’s where it gets interesting! Multiply your QBI by 20% to see your potential reduction. For instance, if your net rental earnings are $50,000, your QBI reduction would be a neat $10,000.
-
Consider Taxable Earnings Limits: Keep in mind that your QBI reduction might hit some limits based on your taxable earnings. If your taxable income goes over certain thresholds, you could face additional restrictions.
-
Use IRS Forms: Finally, when it’s time to file your taxes, you’ll need to complete IRS Form 8995 or 8995-A to report your QBI reduction. These forms will help you navigate the calculations and ensure you’re in line with IRS regulations.
By following these steps, you can nail down your QBI reduction and really maximize those tax savings. And hey, chatting with a tax consultant can give you even more insight into compliance requirements and what you might need to consider to qualify for these benefits. So, what do you think? Ready to tackle your QBI deduction?
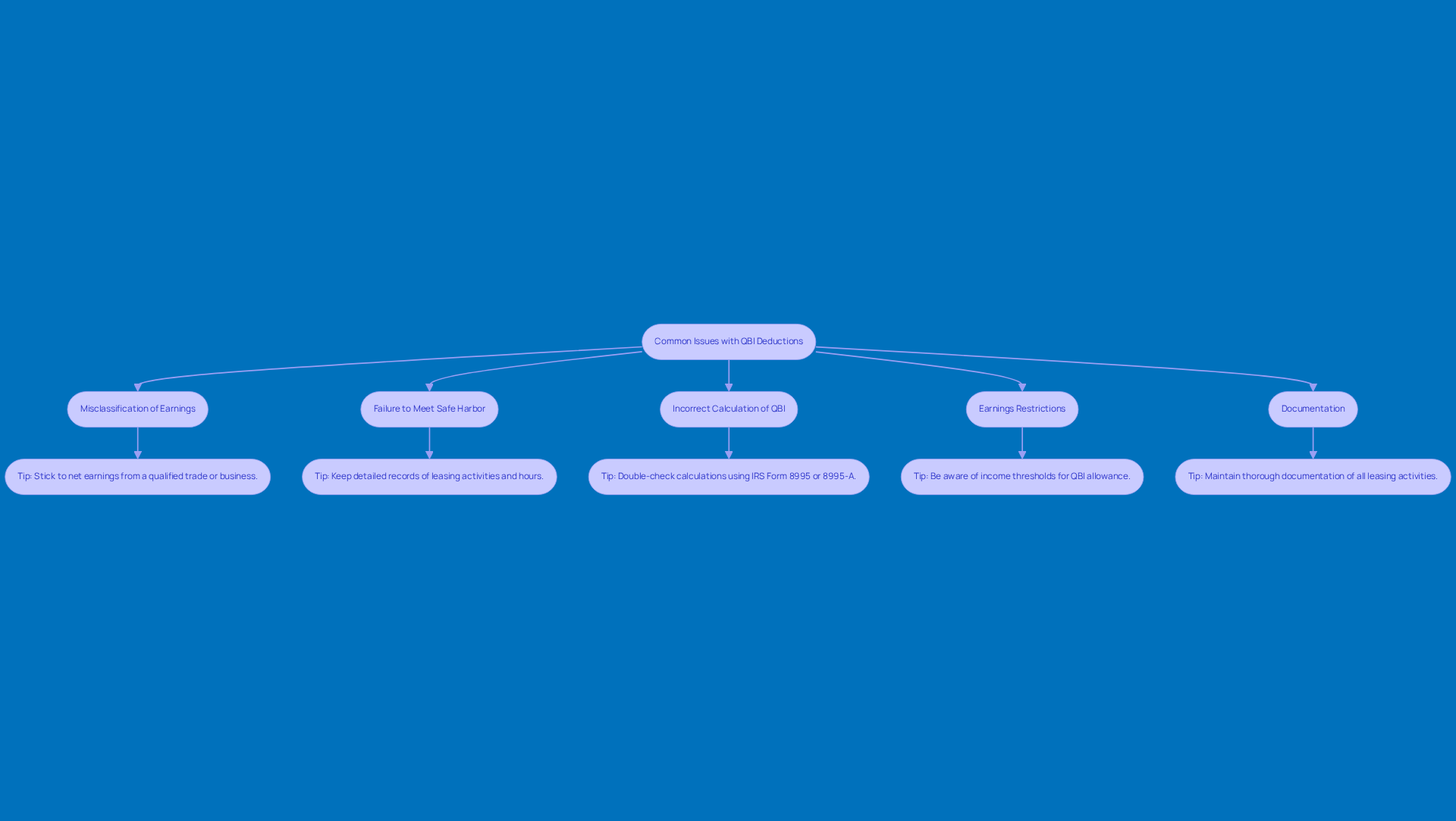
Troubleshoot Common Issues with QBI Deductions for Rental Properties
When you're claiming your deduction for a qualified business income rental property related to property leases, you might run into a few common hiccups. But don’t worry! Here are some handy troubleshooting tips to help you tackle these challenges:
-
Misclassification of Earnings: First off, make sure you’re not mixing in non-business earnings like capital gains or interest revenue when calculating your QBI. Stick to net earnings from a qualified trade or business. Believe it or not, many property owners mislabel their earnings, which can mean missing out on some sweet tax savings.
-
Failure to meet the safe harbor requirements could mean that your leasing income does not qualify as qualified business income rental property. Keep detailed records of your leasing activities and remember the 250-hour requirement if it applies to you. Just a heads up, this requirement is based on qualified business income rental property, not per individual property.
-
Incorrect Calculation of QBI: It’s always a good idea to double-check your calculations for accuracy. You can use IRS Form 8995 or 8995-A to help with this and make sure you’re applying the right percentage for your tax reduction.
-
Earnings Restrictions: Watch out for those earnings thresholds that could limit your QBI allowance. For 2023, single filers with taxable income at or below $182,100 and joint filers at or below $364,200 may qualify for the full 20% reduction. Plus, starting in 2026, there’s a minimum allowance of $400 for qualified business income rental property for taxpayers with at least $1,000 in active QBI. Going over these limits can lead to a reduction or phase-out of your deduction.
-
Documentation: Keep thorough documentation of all your leasing activities, expenses, and income. This is super important if you get audited or need to back up your claims. Keeping records that include dates, service providers, and time spent on rental services can really strengthen your position.
By proactively addressing these common issues, you can boost your chances of successfully claiming the QBI deduction and maximizing your tax benefits. And hey, consulting with a tax professional can really help you understand and comply with QBI regulations!
Conclusion
Understanding and effectively using Qualified Business Income (QBI) can really boost the financial success of rental property owners. By recognizing the potential tax benefits tied to QBI, landlords might be able to deduct up to 20% of their qualified business income from their taxable income. That’s a pretty significant saving! This deduction isn’t just a financial perk; it’s a chance for property owners to fine-tune their tax strategy and enhance their overall profitability.
In this guide, we’ve shared some key insights about the eligibility criteria for QBI. It’s important to be regularly involved in property management, keep separate financial records, and stick to safe harbor requirements. We’ve also laid out the steps for calculating the QBI deduction, highlighting how crucial accurate record-keeping is and how income thresholds can affect the deduction amount. By tackling common issues that pop up during the claims process, property owners can sidestep potential pitfalls and stay compliant with IRS regulations.
So, mastering the ins and outs of Qualified Business Income is essential for landlords who want to maximize their tax benefits and boost their rental property success. By staying updated on eligibility requirements and calculation methods, and by proactively managing common challenges, property owners can make savvy decisions that lead to greater financial stability. Why not take action today? Organizing your records and chatting with tax professionals can set you up for a more prosperous future in rental property management!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Qualified Business Income (QBI)?
Qualified Business Income (QBI) refers to the net earnings generated from a qualified trade or business, which can include leased properties under certain conditions.
Why is understanding QBI important for rental property owners?
Understanding QBI is crucial for property owners because it may allow them to deduct up to 20% of their qualified business income from their taxable income, potentially leading to significant tax savings.
What is required for leasing activity to qualify for the QBI deduction?
To qualify for the QBI deduction, leasing activity must be recognized as a trade or business, which typically requires regular and continuous involvement in leasing operations.
What criteria must one meet to be recognized as a real estate professional for QBI purposes?
To be recognized as a real estate professional, an individual must spend more than half of their total working hours on real estate businesses and at least 750 hours each year in real estate activities.
When is the QBI deduction available?
The QBI deduction is available for tax years starting after December 31, 2017, and ending on or before December 31, 2025.
Can owning multiple rental properties qualify for the QBI deduction?
Owning two qualified business income rental properties, each requiring 125 hours of eligible leasing services per year, does not meet the 250-hour test needed to qualify for the QBI deduction.
How can understanding QBI help landlords?
Understanding QBI can help landlords make informed decisions that enhance their property's profitability and tax efficiency, maximizing potential tax benefits.