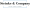Introduction
Navigating the complex world of U.S. tax obligations can feel pretty overwhelming, especially for green card holders. You’ve got to keep track of specific rules about your worldwide income, and that’s no small feat! But don’t worry-this article is here to share some essential strategies and insights that can help you manage your tax responsibilities and even optimize your financial situation.
Now, let’s be real: the thought of hefty penalties for not complying can be nerve-wracking. So, how can you make sure you’re meeting your tax obligations while keeping those liabilities in check? Let’s dive in and explore some friendly tips together!
Explore Tax Obligations for Green Card Holders
If you’ve got a green card, you’re recognized as a lawful permanent resident, and that means you have responsibilities related to taxes for green card holders in the U.S. Yep, you’re required to file yearly tax returns and report your global earnings, no matter where they come from. Let’s break down what you need to know:
- Filing Requirement: First off, you’ll need to file Form 1040, the U.S. Individual Income Tax Return, by April 15 each year. This form is crucial for documenting your earnings and figuring out what you owe in taxes. Missing the deadline? That could lead to some serious penalties, including hefty fines and interest on any unpaid taxes.
- Worldwide Earnings Reporting: You’ve got to report all your earnings-think wages, dividends, rental income from properties abroad, and any other money you make. It’s all about staying compliant with U.S. tax laws. Trust me, understanding the importance of accurate reporting can save you from underpayment penalties, which can really add up if you don’t meet the IRS’s requirements for estimated tax payments.
- Foreign Earned Revenue Exclusion (FEIE): Good news! If you qualify for the FEIE, you can exclude a chunk of your foreign earned income from U.S. taxes. This can really lighten your tax load.
- Reporting Foreign Financial Accounts: Got foreign financial accounts? If the total balance exceeds $10,000 at any point during the year, you’ll need to report them using the Report of Foreign Bank and Financial Accounts (FBAR). Non-compliance? That could mean penalties starting at $10,000.
- Tax Treaties: Some countries have tax treaties with the U.S. that can affect your tax obligations. These treaties might help you avoid double taxation on income earned overseas.
- Safe Harbor Payments: To dodge underpayment penalties, consider safe harbor payments. This means prepaying the lesser of 90% of this year’s tax or 100% of last year’s tax. It’s a smart way to create a cushion against penalties.
- De Minimis Exception: If your total tax obligation minus withholdings and credits is under $1,000, you can completely avoid underpayment penalties. How great is that?
- Penalties for Non-Compliance: Remember, failing to file Form 1040 can lead to serious penalties, including big fines and interest on unpaid taxes. For instance, if you don’t file your FBAR, penalties can start at $10,000 and go up from there.
Understanding these requirements is super important for taxes for green card holders to stay compliant and avoid any hiccups with their immigration status. Plus, keeping accurate records of your earnings and tax filings is key for your financial stability and compliance, so you’re always ready for any IRS inquiries.
Understand Worldwide Income Taxation
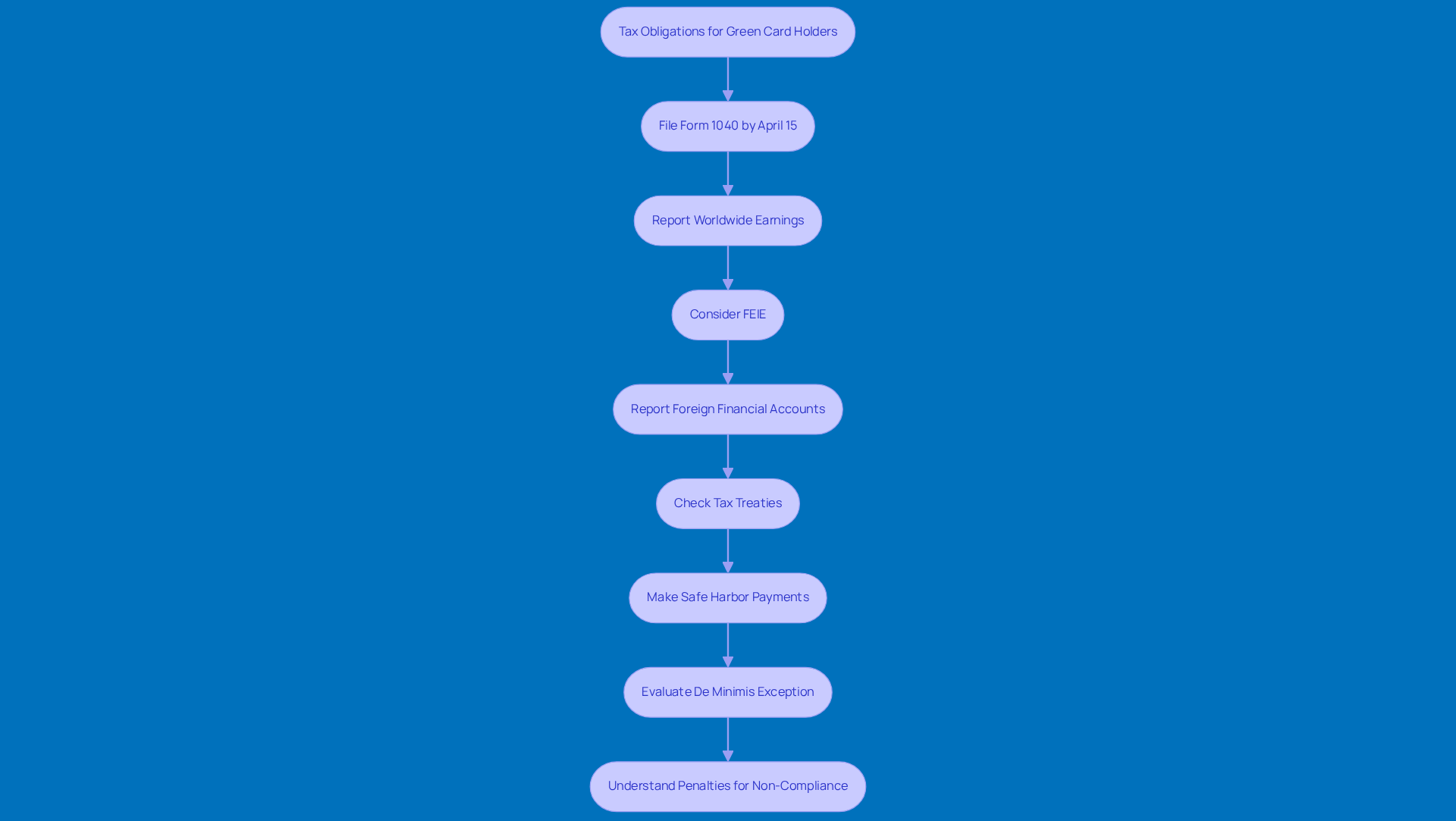
Hey there, green card holders! Did you know that you’re subject to taxes for green card holders on your worldwide income? Yep, that includes a few important areas you should be aware of:
-
Foreign Earned Income: If you’re earning money from a job or business outside the U.S., you need to report it. For instance, let’s say you’re working abroad and make $150,000. You’ll have to let the IRS know about that, but here’s the good news: you can exclude up to $130,000 under the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE) for 2025, as long as you meet certain criteria, like passing the physical presence test or the bona fide residence test.
-
Investment Earnings: This includes dividends, interest, and capital gains from your foreign investments. If you’re getting dividends from a foreign company, you’ll need to report those as part of your taxable income too.
-
Foreign Tax Credit: To help ease the pain of double taxation, you can claim a Foreign Tax Credit (Form 1116) for taxes you’ve paid to foreign governments on income that’s also taxed in the U.S. Many green card holders find this credit really helpful in reducing their overall taxes for green card holders.
-
Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE): For the 2025 tax year, if you qualify, you can exclude up to $130,000 of your foreign earned income from your U.S. taxable income. This can be a real lifesaver for those who meet the necessary tests, helping you keep more of your hard-earned cash while living abroad.
It’s super important to understand the reporting requirements related to taxes for green card holders to stay compliant and avoid any penalties. Make sure you’re accurately declaring all your overseas earnings and taking advantage of the credits and exclusions available to you. It can really help optimize your tax situation!
Implement Strategies to Reduce Tax Liability
If you're a green card holder looking to lighten your tax load, here are some friendly strategies to consider:
- Utilize the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE): Did you know that qualifying for the FEIE lets you exclude up to $130,000 of foreign earned income from U.S. taxes in 2025? This can be a game-changer, especially if you’re living in a low-tax or no-tax country. It really helps to lower your taxable income!
- Claim Foreign Tax Credits (FTC): If you’ve paid taxes to a foreign government, you can claim the FTC to reduce your U.S. tax bill. This is particularly useful if you’re in a country with higher tax rates than the U.S. - it’s like getting a little relief!
- Maximize Deductions: Make sure you’re taking full advantage of deductions available to you, like mortgage interest, student loan interest, and charitable contributions. In 2025, the standard deduction will jump to $15,000 for individuals and $30,000 for married couples filing jointly. That’s a nice boost to lower your taxable earnings!
- Retirement Contributions: Thinking about your future? Contributing to retirement accounts like IRAs can help lower your taxable income while you save for later. The contribution limit for IRAs stays at $7,000 in 2025, making it a smart way to save on taxes.
- Consult a Tax Professional: It’s always a good idea to chat with a tax advisor who knows the ins and outs of international tax laws. They can offer personalized strategies that fit your unique situation, helping you navigate the complexities of U.S. tax obligations while maximizing your benefits.
By putting these strategies into action, green card holders can take charge of their taxes for green card holders and boost their financial well-being. So, why not start exploring these options today?

Navigate Foreign Account Reporting Requirements
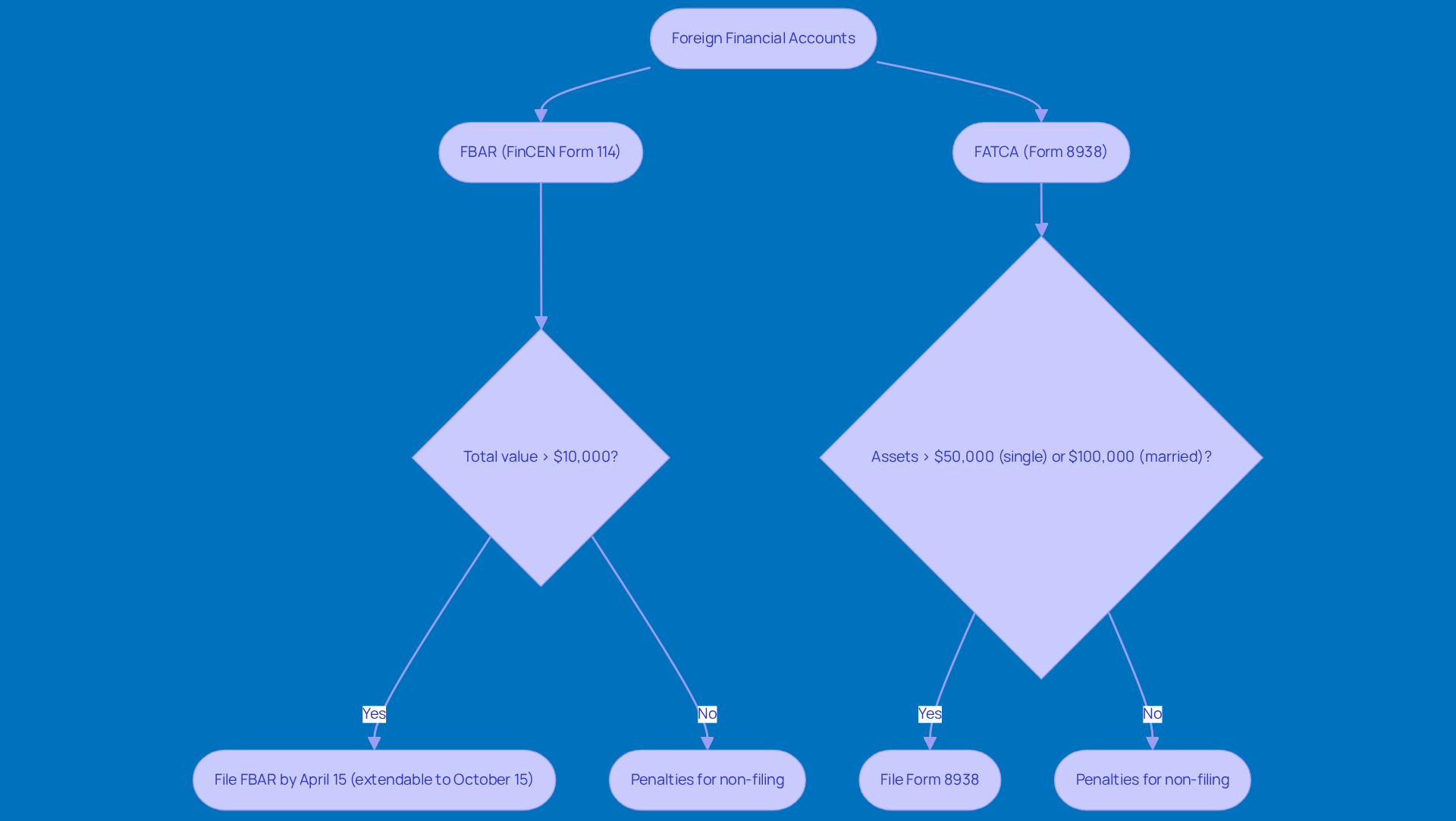
Hey there, green card holders! If you’ve got foreign financial accounts, it’s super important to know about the reporting requirements regarding taxes for green card holders to stay on the right side of U.S. tax laws. Let’s break it down:
-
FBAR (FinCEN Form 114): If the total value of your foreign accounts ever tops $10,000 during the calendar year, you’ve got to file an FBAR. The deadline? April 15, but don’t worry-you can snag an automatic extension until October 15. Just a heads up: if you don’t file, you could face penalties up to $10,000 for non-willful violations. And if it’s willful? Those penalties can skyrocket to $100,000 or even 50% of your account balance. Yikes!
-
FATCA (Form 8938): Now, according to the Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act, you might also need to report your foreign financial assets on Form 8938 if their total value exceeds certain thresholds. For example, if you’re single and living in the U.S., you need to report if your foreign assets exceed $50,000 at year-end or $75,000 at any point during the year. For married couples filing jointly, those numbers jump to $100,000 and $150,000. Not filing can lead to penalties starting at $10,000, plus more if you keep ignoring the IRS after they give you a nudge.
-
Record Keeping: Keeping accurate records of all your foreign accounts is key. Make sure you have details like account numbers, financial institutions, and balances handy. This diligence not only helps you comply but also gets you ready for any potential audits. As CPA Andrew Coleman puts it, "FBAR filing is required if foreign accounts exceed $10,000 at any time."
-
Penalties for Non-Compliance: The stakes are high if you fail to file FBAR or FATCA. Penalties can hit $10,000 for non-willful violations and go much higher for willful ones. It’s crucial to understand and meet the taxes for green card holders to dodge hefty fines and legal troubles. Coleman also reminds us, "You risk back taxes, interest, civil penalties (including FBAR penalties for unreported accounts), and potential audits, though streamlined relief may apply if your noncompliance was non-willful."
As we look ahead to 2025, the reporting requirements are still pretty strict. So, stay informed about your obligations to navigate these complexities effectively. Remember, being proactive can save you a lot of headaches down the road!
Conclusion
Understanding your tax obligations is super important if you’re a green card holder. You’ve got to navigate the sometimes tricky waters of U.S. tax laws. From filing your annual tax returns to reporting your worldwide income, it can feel a bit overwhelming. But don’t worry! Getting a handle on these requirements is key to staying compliant and avoiding any penalties that could mess with your financial stability or immigration status.
So, what should you keep in mind? First off, timely filing and accurately reporting your global earnings are crucial. Plus, don’t forget about the tax benefits available to you, like the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion and the Foreign Tax Credit. And let’s not overlook the foreign account reporting requirements, such as FBAR and FATCA - being aware of these can save you from some serious penalties. By using smart strategies, like maximizing your deductions and consulting with tax professionals, you can manage your tax liabilities effectively.
Ultimately, staying informed and proactive about your tax obligations not only helps you stay compliant but also empowers you to optimize your financial situation. Embracing these strategies can lead to significant savings and peace of mind. This way, you can focus on your personal and professional goals without the stress of tax-related issues hanging over your head. So, why not take control of your tax responsibilities today? It’s a step toward a more secure and prosperous future!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the tax obligations for green card holders in the U.S.?
Green card holders are required to file yearly tax returns and report their global earnings, regardless of where the income comes from.
What form do green card holders need to file for their taxes?
Green card holders must file Form 1040, the U.S. Individual Income Tax Return, by April 15 each year.
What happens if a green card holder misses the tax filing deadline?
Missing the deadline can lead to serious penalties, including hefty fines and interest on any unpaid taxes.
What types of income must green card holders report?
Green card holders must report all earnings, including wages, dividends, rental income from properties abroad, and any other income.
What is the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE)?
The FEIE allows qualifying green card holders to exclude a portion of their foreign earned income from U.S. taxes, potentially reducing their tax burden.
Are green card holders required to report foreign financial accounts?
Yes, if the total balance of foreign financial accounts exceeds $10,000 at any point during the year, they must report them using the Report of Foreign Bank and Financial Accounts (FBAR).
What are the penalties for not reporting foreign financial accounts?
Non-compliance with FBAR reporting can result in penalties starting at $10,000.
How do tax treaties affect green card holders' tax obligations?
Tax treaties between the U.S. and some countries may help green card holders avoid double taxation on income earned overseas.
What are safe harbor payments?
Safe harbor payments allow green card holders to prepay the lesser of 90% of this year's tax or 100% of last year's tax to avoid underpayment penalties.
What is the de minimis exception for underpayment penalties?
If a green card holder's total tax obligation minus withholdings and credits is under $1,000, they can avoid underpayment penalties entirely.
What are the consequences of failing to file Form 1040?
Failing to file Form 1040 can lead to serious penalties, including large fines and interest on unpaid taxes.
Why is it important for green card holders to understand their tax obligations?
Understanding tax obligations is crucial for green card holders to stay compliant and avoid issues that could affect their immigration status. Keeping accurate records of earnings and tax filings is also essential for financial stability.