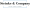Introduction
If you’re a small business owner with a green card, understanding the tax implications can feel like navigating a maze. You’ve got to report your global earnings and deal with some pretty complex filing obligations. It’s no wonder many green card holders find themselves facing significant challenges when it comes to managing their tax liabilities. So, how can you steer through these tricky waters and optimize your financial strategies without running into penalties?
In this article, we’ll dive into the essential tax obligations you need to know, explore potential deductions, and share strategies to help minimize those pesky tax liabilities. Think of it as your go-to guide for securing your financial future as a green card holder!
Clarify Tax Obligations for Green Card Holders
As a permanent resident, you’re considered a tax resident in America, and this includes understanding the green card tax implications, meaning you need to declare your global earnings to the IRS. Yep, that includes money you make both inside and outside the U.S. Let’s break down the essentials:
- Filing Requirements: If you hold a green card, you’ve got to file a U.S. tax return (Form 1040) every year, no matter where you live or where your income comes from. In 2026, it’s estimated that about 90% of green card holders will comply with this requirement, reflecting a solid commitment to understanding the green card tax implications.
- Tax Rates: You’ll be taxed at the same rates as American citizens, and those rates vary based on how much you earn. Getting a handle on these rates is super important for smart financial planning.
- Deductions and Credits: Good news! You might qualify for some deductions and credits, like the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE). This nifty exclusion lets you leave out up to $130,000 of foreign earnings from U.S. taxes if you meet certain residency tests. That can really help lower your taxable income.
- Penalties for Non-Compliance: Not filing your return? That could lead to some hefty penalties, including fines and interest on any unpaid taxes. Plus, ignoring these obligations could jeopardize your immigration status, so it’s crucial to stay informed about the green card tax implications and remain compliant with your tax duties.
- Expert Insights: Tax pros emphasize how important it is to understand these requirements. As one expert put it, 'Green residents are required to pay U.S. taxes on global earnings,' which underscores the green card tax implications and the need to follow the rules to avoid any legal headaches.
So, keep these points in mind, and make sure you’re on top of your tax game!
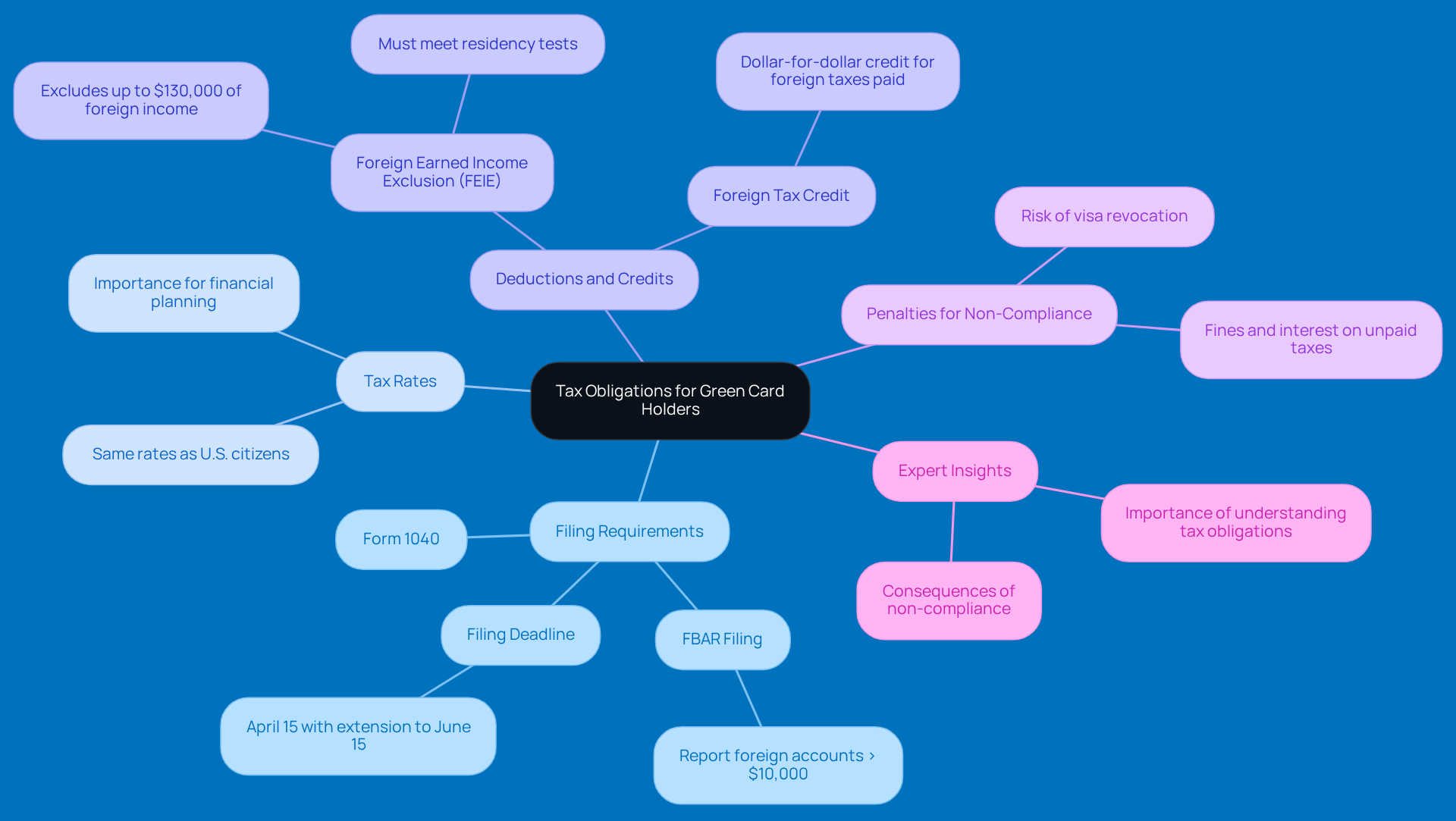
Explore Worldwide Income Taxation Implications
Hey there, green card holders! Did you know that, because of green card tax implications, you need to report all your earnings from around the globe? Yep, that includes wages, dividends, interest, and even rental income. It’s super important to get a handle on the green card tax implications for both compliance and your financial planning.
-
What’s Worldwide Earnings?: This term covers all revenue from any source, whether it’s from right here at home or abroad. For instance, if you’re raking in cash from a business overseas, you’ve got to include that on your American tax return.
-
Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE): If you’re a qualifying green card holder for the 2026 tax year, you can exclude up to $132,900 of foreign earned income from U.S. taxes. To be eligible, you’ll need to pass certain residency tests, like the Bona Fide Residence Test or the Physical Presence Test.
-
Foreign Tax Credit: Paying taxes to a foreign government? Good news! You might qualify for a credit against your U.S. tax bill, which can help you avoid being taxed twice on the same income.
-
Reporting Requirements: Don’t forget about additional reporting obligations, like the Foreign Bank Account Report (FBAR). If the total balance of your foreign bank accounts exceeds $10,000 at any point during the year, you need to file this report. Ignoring this can lead to some hefty penalties.
These updates highlight the ongoing changes in tax policy aimed at helping expatriates. So, it’s crucial for green card holders to stay informed and proactive about the green card tax implications in their tax planning. Got questions? Don’t hesitate to reach out!
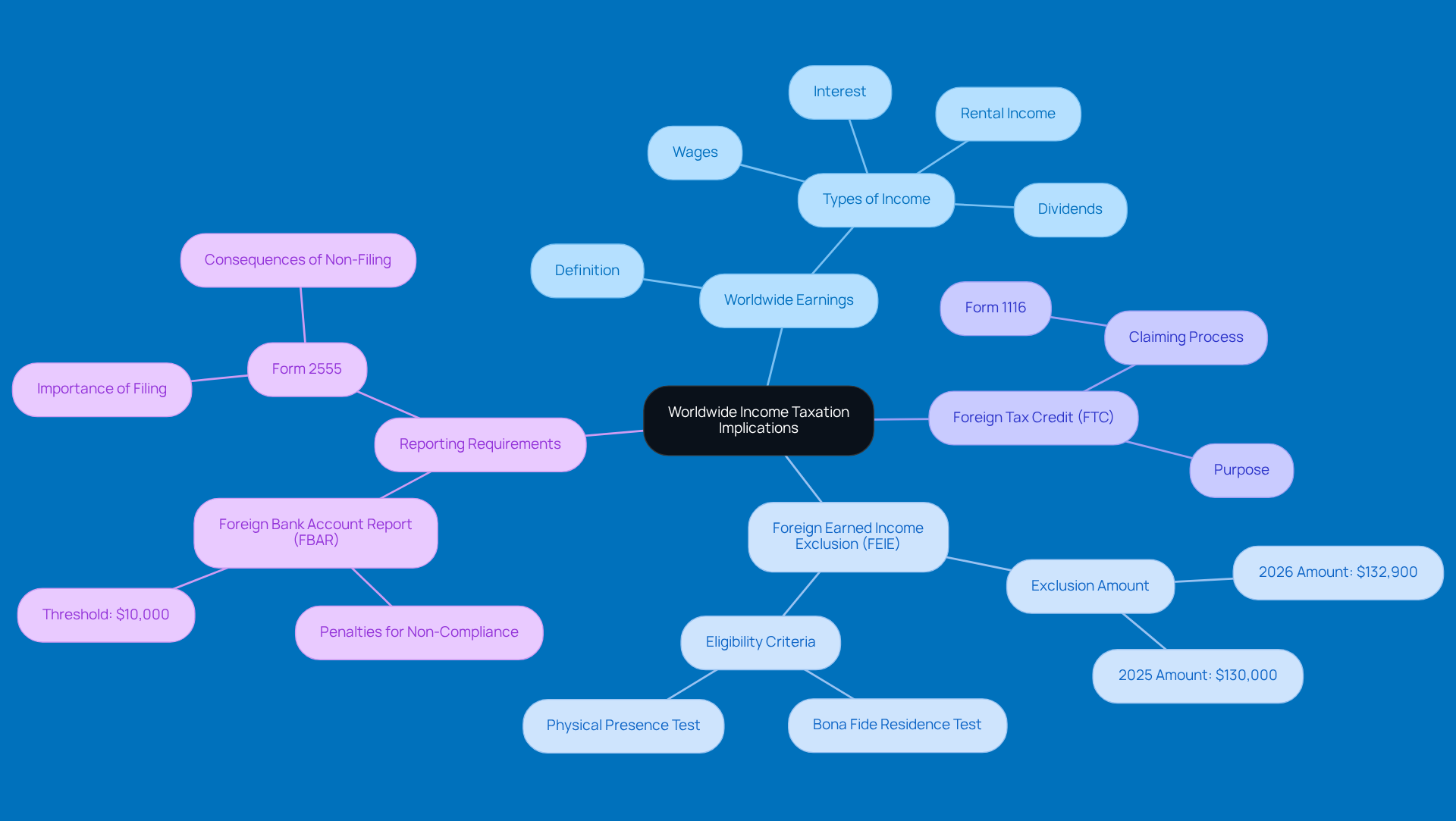
Implement Strategies to Reduce Tax Liability
If you're a green card holder looking to minimize your tax liability, here are some friendly strategies to consider:
- Maximize Deductions: First off, take a good look at all those business expenses you can deduct from your taxable income. Think about the essentials-supplies, travel, and even home office costs. Properly categorizing these expenses is key to getting the most out of your deductions.
- Utilize Retirement Accounts: Have you thought about contributing to retirement accounts like a 401(k) or IRA? Not only does this help secure your financial future, but it also lowers your taxable income. Business owners can actually contribute more to these accounts than traditional employees, which means more savings come tax time.
- Consider Entity Structure: The way your business is structured-whether it’s an LLC, S-Corp, or something else-can really affect your tax liability. Chatting with a financial expert can help you find the best setup for your unique situation, which may lead to better deductions, lower taxes, and a better understanding of green card tax implications.
- Plan for Estimated Taxes: If you think you’ll owe more than $1,000 in taxes, it’s smart to make estimated tax payments throughout the year. This proactive move can help you dodge penalties and interest, keeping your financial planning on track.
- Stay Informed on Tax Law Changes: Tax laws change all the time, and staying updated can help you snag new deductions or credits. For instance, understanding the Qualified Business Income (QBI) deduction could lead to some serious savings for eligible small business owners.
- Leverage Professional Guidance: Finally, don’t underestimate the value of a tax advisor. They can offer personalized insights on maximizing deductions and navigating the sometimes tricky tax regulations. This expert advice is especially handy as you gear up for the upcoming tax year and think about strategies for 2026 and beyond.
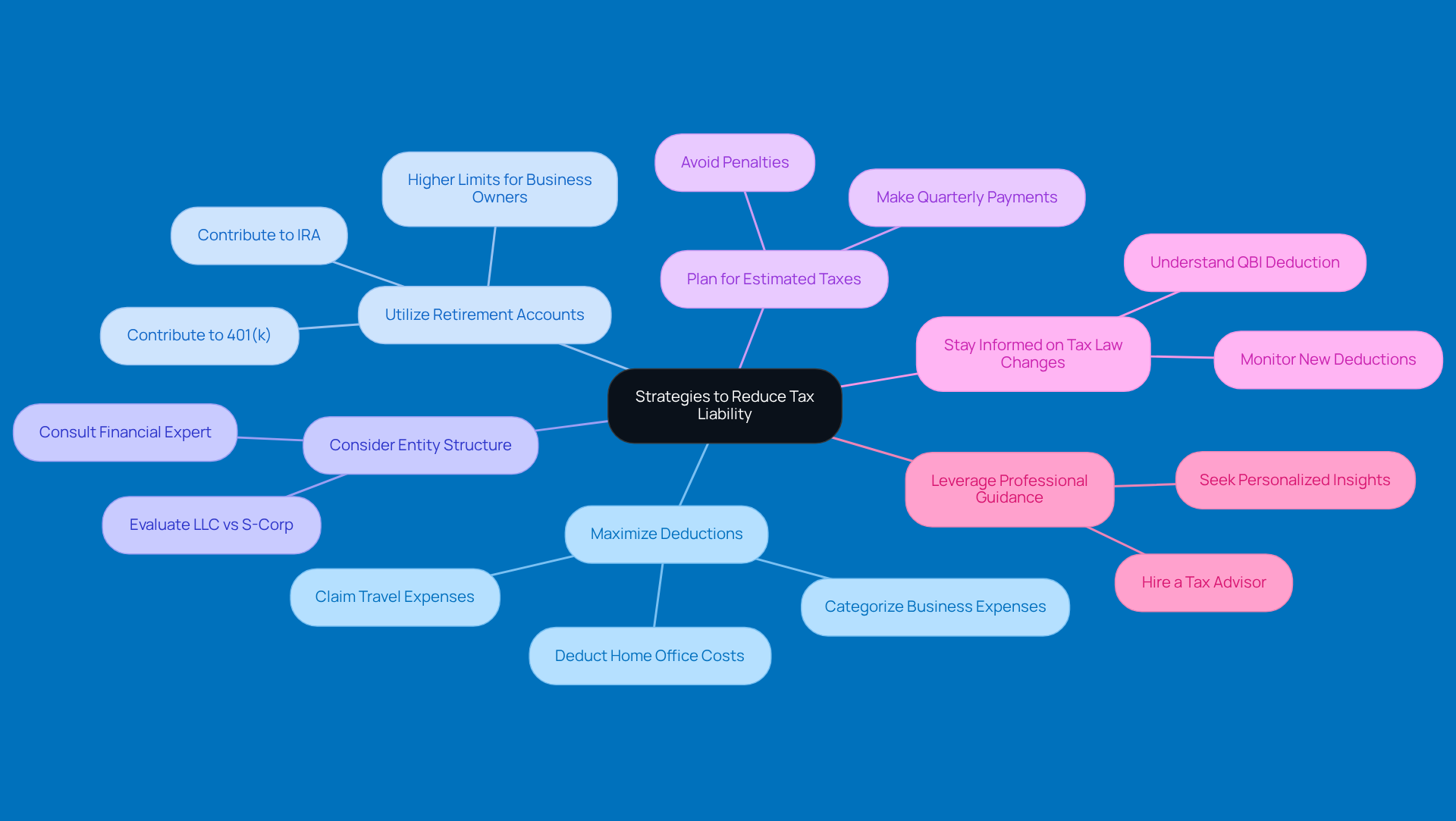
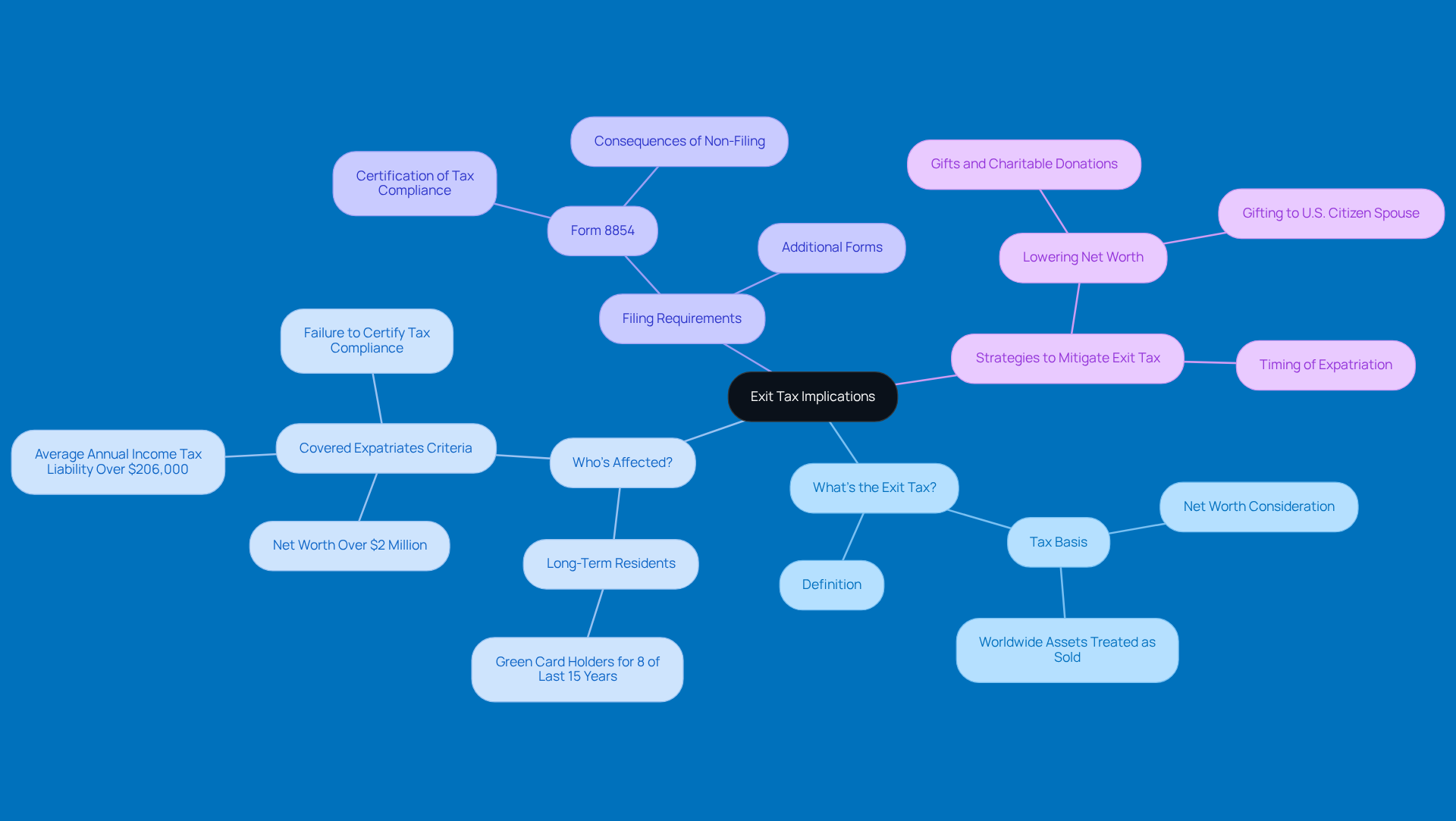
Understand the Exit Tax and Its Implications
If you've held a green card for 8 of the last 15 years, giving up your status might trigger green card tax implications. Here’s what you should know:
-
What’s the Exit Tax? The exit tax is a fee that applies to certain folks who decide to give up their green card. It’s based on your net worth and tax obligations when you expatriate. Basically, it treats your worldwide assets as if they were sold the day before you let go of your green card, which could result in significant green card tax implications and hefty tax bills.
-
Who’s Affected? Generally, long-term residents-those who’ve had a green card for 8 out of the last 15 years-might face this tax. If your net worth is over $2 million or if you’ve had an average annual income tax liability exceeding $206,000 in the past five years, you could be classified as a covered expatriate, which means the exit tax applies to you.
-
Filing Requirements: To stay on the right side of the exit tax rules, you’ll need to file Form 8854. This form certifies that you’ve met your American tax obligations for the last five years. If you don’t file it, you might automatically be classified as a covered expatriate, which can lead to some serious penalties.
-
Strategies to Mitigate Exit Tax: Think about lowering your net worth below the $2 million mark through gifts or charitable donations before you give up your green card. Plus, if you gift to a U.S. citizen spouse, you can do so without triggering gift tax-definitely a strategy worth considering! With some proper planning, you can minimize those potential exit tax liabilities.
Understanding these points is super important for green card holders considering the green card tax implications of relinquishing their status. The implications can be significant, so it’s worth taking the time to get informed!
Conclusion
Navigating the tax landscape as a green card holder is super important for staying compliant and making the most of your financial benefits. It’s crucial to understand the tax implications that come with your green card, like global income reporting, tax rates, and potential deductions that can really affect your overall tax bill.
Let’s break it down: you need to file a U.S. tax return no matter where your income comes from. You might also be eligible for the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion, which is a nice perk! Plus, having a solid financial plan can help you keep those tax burdens in check. And don’t forget, not complying can lead to penalties and even put your immigration status at risk. That’s why getting professional tax advice is key to optimizing your tax strategies.
For green card holders, staying on top of your tax obligations and finding ways to reduce your liability isn’t just a good idea - it’s a must! With the right knowledge and a bit of proactive planning, you can tackle your tax responsibilities more effectively. This can lead to better financial outcomes and a whole lot of peace of mind. So, why not embrace these insights? Taking control of your tax situation means you can stay compliant while maximizing your financial potential!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the tax obligations for green card holders in the U.S.?
Green card holders are considered tax residents in America and must declare their global earnings to the IRS, filing a U.S. tax return (Form 1040) every year regardless of where they live or earn income.
Do green card holders have to file a tax return even if they live outside the U.S.?
Yes, green card holders must file a U.S. tax return every year, no matter where they live or where their income comes from.
What tax rates do green card holders pay?
Green card holders are taxed at the same rates as American citizens, which vary based on their income levels.
Are there any deductions or credits available for green card holders?
Yes, green card holders may qualify for deductions and credits, such as the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE), which allows them to exclude up to $130,000 of foreign earnings from U.S. taxes if they meet certain residency tests.
What are the consequences of not filing a tax return as a green card holder?
Not filing a tax return can result in hefty penalties, including fines and interest on unpaid taxes, and could jeopardize immigration status.
Why is it important for green card holders to understand their tax obligations?
Understanding tax obligations is crucial to avoid legal issues and comply with U.S. tax laws, as green card holders are required to pay taxes on their global earnings.