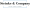Overview
Let’s chat about something that’s super important for rural businesses: understanding primary producers and their ecological roles. You might be wondering, why should I care? Well, primary producers, like plants and phytoplankton, are the backbone of our ecosystems. They help keep everything in balance, which directly impacts agricultural productivity and sustainability practices. This means better crop yields and stronger operational resilience for rural entrepreneurs like you!
Think about it: when ecosystems are healthy, farmers can grow more food and do it in a way that’s good for the planet. It’s a win-win! So, how can you leverage this knowledge in your business strategies? By recognizing the vital role these producers play, you can make smarter decisions that not only benefit your bottom line but also contribute to a healthier environment.
Incorporating this understanding into your business approach can lead to innovative practices that enhance productivity. So, what’s stopping you from diving deeper into this topic? Let’s explore how you can harness the power of primary producers to boost your rural business! Remember, it’s all about connecting the dots between nature and your entrepreneurial journey.
Introduction
Let’s dive into the fascinating world of life on Earth, starting with the incredible role of primary producers. These unsung heroes of our ecosystems are the ones who take sunlight and chemical energy and turn it into the organic matter that fuels everything around us. They’re the backbone of agricultural success and environmental health!
As more rural businesses look for sustainable practices, it’s worth asking: how can we harness the power of these primary producers to boost productivity while also ensuring we’re ready for the climate challenges ahead? It’s a big question, but one that’s crucial for our future. So, let’s explore this together!
Define Primary Producers and Their Ecological Role
Hey there! Let’s talk about primary producers, also known as autotrophs by some people. These amazing organisms can whip up their own food through processes like photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. They are the primary producers in the food chain, converting sunlight or chemical energy into organic matter that consumers in the ecosystem depend on. In our terrestrial ecosystems, plants, trees, and some microorganisms can be considered as primary producers. Meanwhile, in our aquatic environments, phytoplankton and algae serve as primary producers. Understanding their role is super important for rural businesses, especially in agriculture, since these guys help keep ecosystems healthy, which in turn supports farming and livestock activities. Their well-being directly impacts crop yields and livestock productivity, so it’s essential for business owners to recognize and support primary producers within these ecological systems.
Now, here’s something interesting: recent advancements in AI-driven crop health monitoring and precision agriculture have shown that farms using sustainable practices that benefit our primary producers can see a whopping 25% boost in crop yields! That’s a pretty compelling reason to nurture these ecological systems, right? Plus, these primary producers are essential for maintaining soil health and water quality, both of which are crucial for sustainable agriculture. As climate change shakes things up—like increasing heavy rainfall that can lead to soil erosion and nutrient loss—the resilience of these primary producers becomes even more critical. Farmers who adopt practices that protect and enhance primary producers not only contribute to environmental sustainability but also bolster their own operational resilience. So, let’s not forget: supporting the health of primary producers isn’t just good for the planet; it’s a smart move for rural entrepreneurs too!
Explore Types of Primary Producers: Terrestrial and Aquatic
When we talk about primary producers, we can break them down into two main types: terrestrial and aquatic.
Terrestrial Primary Producers: Think of all the land-based plants out there—grasses, shrubs, and trees. These guys are super important for carbon fixation and keeping our soil healthy. Plus, they provide food and homes for a bunch of different species. If you’re running a countryside business, knowing about the types of land-based creators in your area can really help you make smart choices about what crops to grow and how to manage your land sustainably. By understanding the local terrestrial creators, rural enterprises can adopt land management strategies that not only boost productivity but also keep the ecological balance in check.
Aquatic Primary Producers: Now, let’s dive into the water! This group mainly includes phytoplankton, algae, and aquatic plants. They’re crucial for maintaining water quality and pumping out oxygen in aquatic ecosystems. If you’re in the fishing or aquaculture business, getting to know the different types of aquatic cultivators can help you manage fish populations and stick to sustainable practices that meet environmental regulations. Did you know that estuarine habitats support about 68% of the U.S. commercial fish harvest? That really shows how vital these aquatic systems are for the fishing industry!
By getting a grip on both types of primary producers, rural entrepreneurs can better align their practices with ecological health, which could lead to improved productivity and a stronger commitment to sustainability. Plus, experts say that nutrient input from marine life, like baleen whales, really boosts ocean productivity. This just goes to show how interconnected our terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems are!

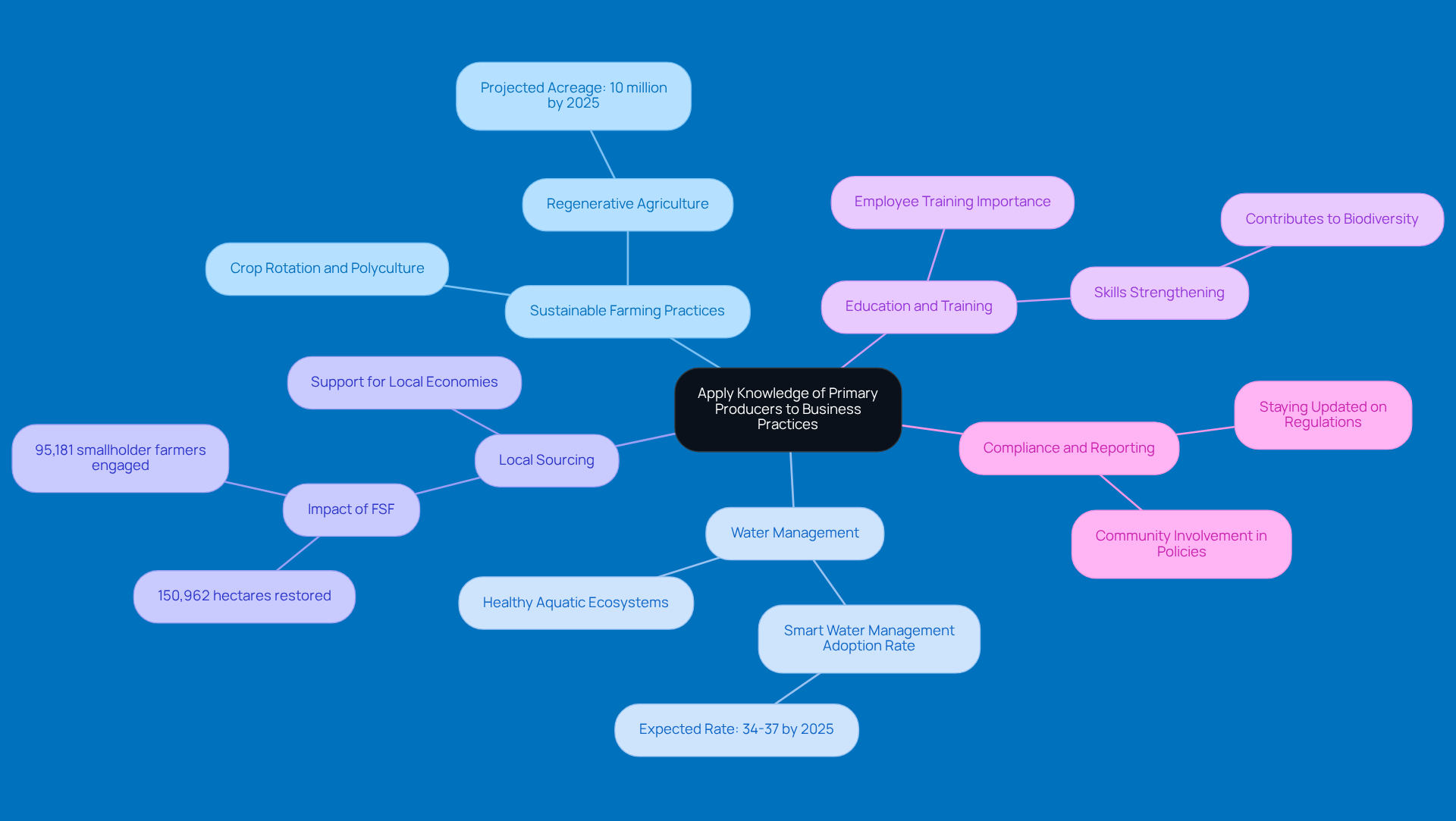
Apply Knowledge of Primary Producers to Business Practices
Understanding essential creators can really boost the sustainability and profitability of rural ventures. Here are some actionable strategies to consider:
-
Sustainable Farming Practices: Ever thought about crop rotation and polyculture? Not only do they enhance soil health, but they also increase biodiversity. This approach helps essential organisms thrive, boosts crop yields, and cuts down on chemical fertilizers, making for a more resilient agricultural ecosystem. Fun fact: the U.S. Department of Agriculture predicts that regenerative agriculture acreage in the U.S. will surpass 10 million acres by 2025, showing a swift move towards sustainable practices.
-
Water Management: If you're in aquaculture or fishing, understanding aquatic foundational organisms is key. Healthy phytoplankton and aquatic plants lead to better fish health and productivity. By managing water effectively—like keeping nutrient levels just right and reducing pollution—you can significantly enhance aquatic ecosystems. Did you know that the adoption rate for Smart Water Management is expected to be between 34-37% by 2025? That’s a clear sign that more folks are recognizing its importance.
-
Local Sourcing: How about promoting locally sourced suppliers in your supply chain? This not only supports local economies but also cuts down on transportation costs. Plus, it aligns perfectly with sustainable business strategies and strengthens community ties. The Food Securities Fund (FSF) has shown the power of local sourcing, restoring 150,962 hectares of land and engaging 95,181 smallholder farmers. Talk about community impact!
-
Education and Training: Investing in employee training about the importance of essential suppliers and sustainable methods can really pay off. When your team is informed, they can make better decisions and foster a culture of sustainability within your organization. As Ousseni Porgo, CEO of gebana Burkina Faso, points out, strengthening farmers’ skills through training directly contributes to biodiversity and environmental protection.
-
Compliance and Reporting: Staying updated on regulations regarding environmental impact and sustainability is crucial. Understanding the role of primary producers helps you meet compliance obligations, thereby avoiding fines and promoting responsible practices. The Subcommittee on Aquaculture emphasizes the importance of community involvement in developing responsible aquaculture policies, highlighting how knowledgeable enterprises play a vital role in compliance initiatives.
By applying these strategies, rural business owners can not only enhance their operational efficiency but also make a positive impact on local ecosystems. So, why not take a step towards long-term sustainability and profitability today?
Conclusion
Understanding primary producers is super important for anyone in rural business. These organisms are the backbone of our ecosystems! They take sunlight and chemical energy and turn it into organic matter, which not only supports the food chain but also boosts agricultural productivity and sustainability. When we recognize their importance, we can make smarter decisions that benefit both the environment and our business operations.
Let’s break it down: there are two main types of primary producers—terrestrial and aquatic.
- Terrestrial producers, like plants and trees, are essential for soil health and carbon fixation.
- Aquatic producers, such as phytoplankton and algae, play a key role in keeping our water quality in check and supporting fish populations.
By implementing sustainable practices that nurture these producers, we can see improved crop yields and stronger operational resilience, especially with all the cool advancements in agricultural technology.
Ultimately, the health of primary producers has a direct impact on rural economies and ecosystems. By adopting sustainable farming practices, managing water effectively, and sourcing locally, rural entrepreneurs can not only boost their business profitability but also contribute to the well-being of their communities and the environment. Embracing the role of primary producers in our business strategies isn’t just a smart move; it’s a necessary step toward a sustainable future for agriculture and rural development. So, let’s get on board and make a difference together!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are primary producers?
Primary producers, also known as autotrophs, are organisms that create their own food through processes like photosynthesis or chemosynthesis.
What role do primary producers play in the ecosystem?
Primary producers are at the base of the food chain, converting sunlight or chemical energy into organic matter that consumers in the ecosystem depend on.
Can you give examples of primary producers in different ecosystems?
In terrestrial ecosystems, examples of primary producers include plants, trees, and some microorganisms. In aquatic environments, phytoplankton and algae serve as primary producers.
Why is understanding primary producers important for rural businesses, particularly in agriculture?
Understanding primary producers is crucial because they help maintain healthy ecosystems, which support farming and livestock activities. Their well-being directly impacts crop yields and livestock productivity.
How can sustainable practices benefit primary producers and agriculture?
Farms that use sustainable practices benefiting primary producers can experience a significant boost in crop yields, with reports of up to a 25% increase.
What additional benefits do primary producers provide for agriculture?
Primary producers are essential for maintaining soil health and water quality, both of which are critical for sustainable agriculture.
How does climate change affect primary producers and agriculture?
Climate change can lead to increased heavy rainfall, resulting in soil erosion and nutrient loss, making the resilience of primary producers even more critical for sustainable agricultural practices.
What should farmers do to support primary producers?
Farmers should adopt practices that protect and enhance primary producers to contribute to environmental sustainability and bolster their operational resilience.