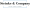Introduction
Navigating the world of taxation can feel overwhelming for any business, right? With all the changes happening in indirect taxes like VAT and GST, it’s no wonder many feel lost. That’s where an indirect tax manager steps in. They’re not just about compliance; they can turn tax practices into real strategic advantages for your business.
So, how can you tap into the expertise of these professionals? Think about it: enhancing your financial health and boosting operational efficiency while steering clear of those pesky penalties. Understanding the role of an indirect tax manager is crucial for any company looking to thrive in today’s complex regulatory landscape. Let’s dive in and explore how this can work for you!
Define the Role of an Indirect Tax Manager
An indirect tax manager plays a key role in handling a company's indirect tax responsibilities, which include taxes like Value Added Tax (VAT), Goods and Services Tax (GST), and sales tax. This position is super important for the indirect tax manager to ensure the company adheres to all tax regulations, files taxes on time, and develops smart strategies to keep tax liabilities in check. Think of the indirect tax manager as the bridge between the company and tax authorities, ensuring that all indirect tax processes are spot on.
Navigating the maze of tax laws can be tricky, especially since they can vary a lot from one place to another. An indirect tax manager not only manages compliance but also seeks to proactively transform tax practices. For example, with more businesses jumping on the Continuous Transaction Controls (CTC) bandwagon, real-time compliance is becoming a must. By 2030, CTC is expected to be the norm in tax administration, making the Tax Manager's role even more crucial for getting tax accuracy right from the start-because once those numbers are in, there’s no going back!
But wait, there’s more! Effective management by an indirect tax manager can really pay off for rural companies. It helps them use their resources better and steer clear of potential legal headaches and financial penalties that come with non-compliance. Industry experts point out that the best tax professionals today aren’t just about processing returns; they’re also focused on ensuring data accuracy and using technology to turn manual processes into strategic insights. This really underscores how vital the indirect tax manager is in fostering a culture of compliance and smart financial planning within the organization.
Outline Key Responsibilities of an Indirect Tax Manager
An indirect tax manager plays a crucial role in ensuring that a company complies with tax regulations and maximizes its tax strategy. Let’s break down some key responsibilities:
-
Compliance Management: This role is all about making sure the company sticks to all the relevant indirect tax laws and regulations. The manager oversees the timely filing of tax returns and payments. Did you know that 62% of businesses are found non-compliant during audits? That’s why the indirect tax manager role is crucial for keeping the financial ship steady.
-
Tax Strategy Development: Crafting and rolling out tax strategies that boost the company’s tax position while keeping liabilities low is essential. It’s about analyzing transactions and advising on tax implications for new business initiatives. This aligns perfectly with the trend of weaving tax into enterprise risk management.
-
Audit Coordination: The indirect tax manager prepares for tax audits by keeping accurate records and documentation, and they represent the company during the audit process. Being audit-ready is key because regulatory slip-ups can really shake things up.
-
Stakeholder Collaboration: Working closely with internal departments like finance and operations is vital. This ensures that the indirect tax manager is involved in tax considerations as part of business decisions. Establishing regular communication can break down barriers and help everyone stay on the same page.
-
Risk Assessment: Spotting and tackling potential tax risks tied to business operations, including cross-border transactions and shifts in tax legislation, is a big part of the job. As non-direct tax experts increasingly see adherence as a bigger challenge than technology, proactive risk management becomes essential.
-
Training and Guidance: Providing instruction and support to staff on secondary tax issues keeps the organization in the loop about regulatory requirements and best practices. This educational role is key to fostering a culture of adherence within the organization.

Explain the Importance of Indirect Tax Managers in Business Strategy
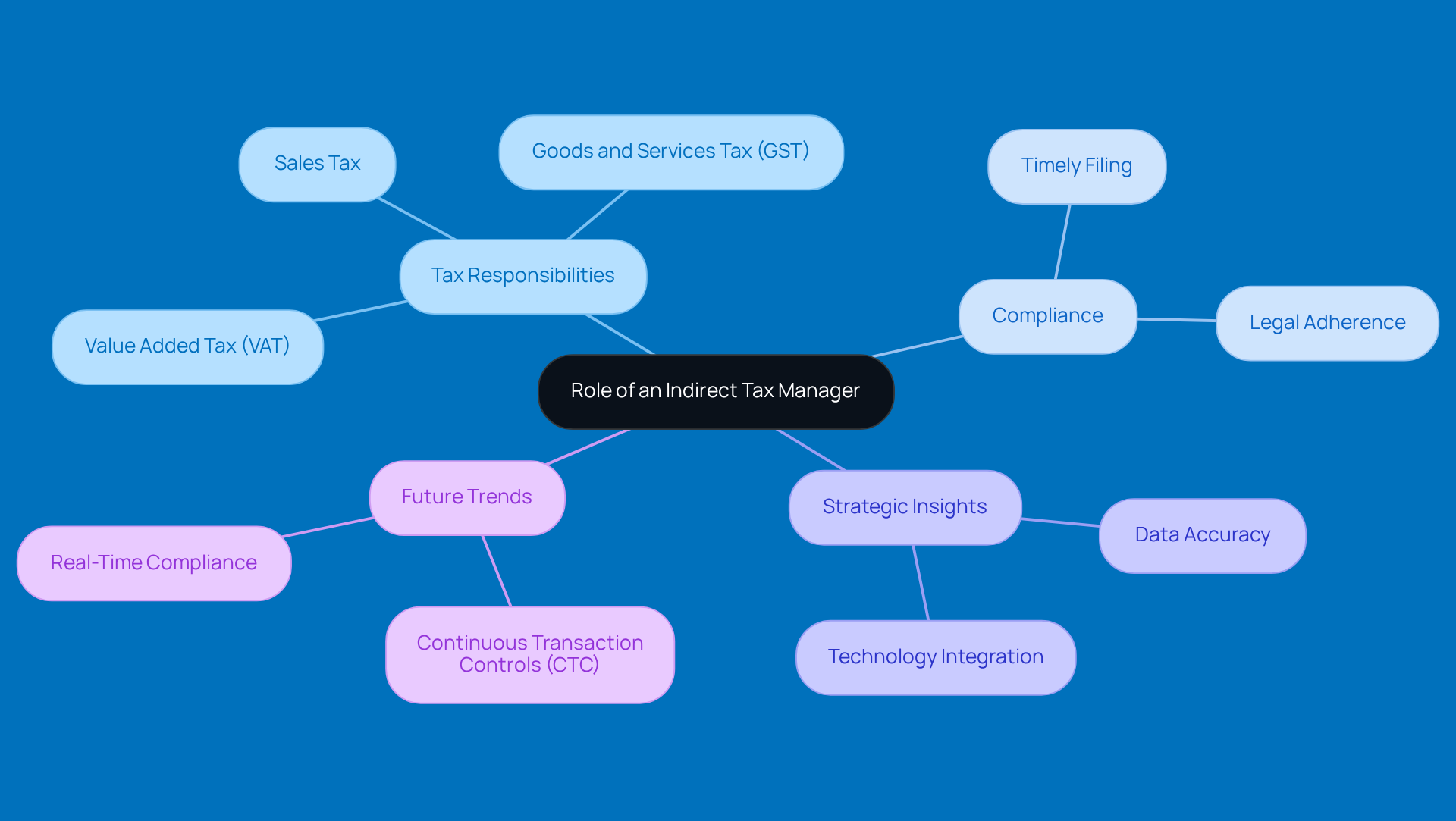
The role of an indirect tax manager is crucial in shaping a company’s business strategy. They make sure tax considerations are woven into operational and financial planning without a hitch. Their know-how is crucial for navigating the tricky waters of non-direct taxes, which can really impact cash flow and profitability. By proactively managing secondary tax responsibilities, these pros can spot opportunities for tax savings and boost efficiency in compliance. For example, a well-thought-out tax strategy can seriously improve cash flow management. Plus, staying on top of compliance helps avoid those pesky penalties and interest fees that can eat into profits.
Now, let’s talk about underpayment penalties - this is a big deal. The IRS hits taxpayers with these penalties when they don’t pay enough of their tax liability through withholding or estimated payments during the year. With the interest rate for underpayments sitting at 8% per year, compounded daily, the stakes are pretty high for small business owners. That’s where the role of an indirect tax manager comes in. They can help businesses meet IRS requirements, like paying at least 90% of the current year’s tax liability or 100% of the previous year’s tax, helping to dodge those penalties. They can also share tips on strategies like the de minimis exception, which lets taxpayers off the hook for penalties if their total tax liability minus withholdings and credits is under $1,000, and safe harbor payments, which protect taxpayers from penalties if they hit certain prepayment thresholds.
But wait, the indirect tax manager has even more information! The role of the indirect tax manager is vital in risk management as they spot potential tax liabilities and advise on ways to mitigate them. In today’s global economy, where businesses are often venturing into diverse markets with different tax rules, their insights are more important than ever. Research shows that effective non-direct tax management can lead to a 15% boost in client retention rates in CPA firms. That’s a pretty compelling reason to pay attention to strategic tax oversight!
Ultimately, the strategic insights from the indirect tax manager not only bolster a company’s financial health but also enhance its competitive edge in the marketplace. By aligning tax strategies with business goals, these professionals help companies navigate the complexities of taxation while maximizing profitability. So, if you’re in the game, it might be time to have a conversation with an indirect tax manager!
Discuss the Evolution and Context of Indirect Tax Management
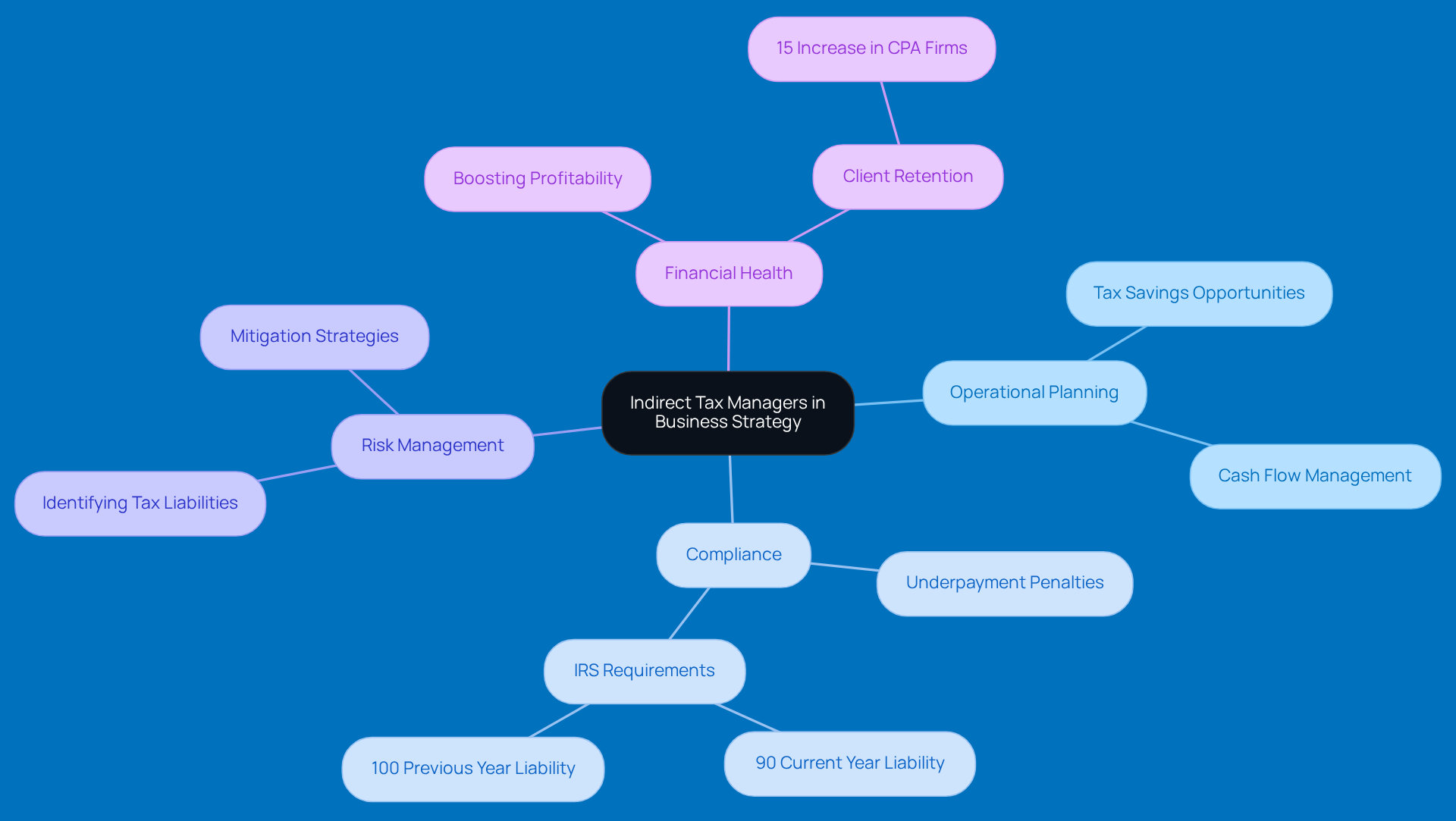
You know, the roots of non-direct revenue management actually go way back to ancient societies, where they first started implementing consumption levies. Over time, though, things have gotten a bit more complicated, especially with the introduction of VAT and GST systems in various countries. These systems were designed to make tax collection easier and improve compliance, but they also brought a whole new set of challenges for businesses, particularly those in rural areas. Just think about it: rural businesses often struggle with limited resources and a lack of understanding when it comes to navigating the complex tax landscape, which can lead to regulatory headaches and financial stress.
Fast forward to today, and the rise of e-commerce and globalization has made the role of the indirect tax manager even trickier. Companies now have to deal with a patchwork of regulations across different jurisdictions, which can feel overwhelming, especially for small businesses. As Brian Gardner, the Director of Global Indirect Tax at Adobe, puts it, "With the global tax landscape presenting numerous challenges for today’s tax department, ONESOURCE Determination offers a centralized approach for enhanced adherence, accuracy, and control."
And let’s not forget how the digital economy has pushed tax authorities to rethink their strategies. This shift has led to increased scrutiny and regulatory demands for businesses. For example, Adobe revamped its tax process, slashing tax return preparation time from two weeks down to just 30 minutes! That’s a perfect illustration of how technology can help ease some of the burdens companies face.
Because of all this, the role of the indirect tax manager has evolved into something much more strategic. As an indirect tax manager, they now need to stay on top of regulatory changes and use technology to streamline compliance processes. Looking ahead, it seems like the future of indirect tax management will be all about greater automation and data analytics, allowing businesses to respond more effectively to the ever-changing tax landscape. This shift really highlights the need for skilled tax professionals who can navigate the complexities of modern tax systems and help businesses stay compliant while boosting their operational efficiency.
Conclusion
An indirect tax manager plays a crucial role in today’s business world, acting as a key bridge between companies and tax authorities. This position isn’t just about ticking boxes for compliance; it’s about strategically shaping a company’s financial future. By expertly navigating the complexities of indirect taxes like VAT and GST, these managers help organizations stay financially healthy and competitive.
Throughout this article, we’ve highlighted some of the key responsibilities of an indirect tax manager. They manage compliance, develop tax strategies, coordinate audits, and assess risks. Their proactive approach in spotting tax-saving opportunities and reducing risks showcases how vital they are in boosting operational efficiency and nurturing a culture of compliance within the organization. As the tax landscape shifts - especially with the growth of e-commerce and globalization - this role is becoming even more important.
The insights shared here really emphasize why businesses should treat indirect tax management as a strategic priority. Companies that weave tax considerations into their overall business strategy can enjoy benefits like improved cash flow, lower liabilities, and better decision-making. So, embracing the expertise of an indirect tax manager isn’t just about compliance; it’s a smart investment that can pave the way for long-term success and resilience in our ever-changing economic landscape.
So, what do you think? Is your organization ready to take that step? Let’s chat about how you can make indirect tax management a part of your strategy!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary role of an indirect tax manager?
The primary role of an indirect tax manager is to handle a company's indirect tax responsibilities, which include taxes like Value Added Tax (VAT), Goods and Services Tax (GST), and sales tax. They ensure compliance with tax regulations, timely filing of taxes, and the development of strategies to manage tax liabilities.
Why is the indirect tax manager considered important for a company?
The indirect tax manager is important because they act as a bridge between the company and tax authorities, ensuring that all indirect tax processes are accurate and compliant. Their role is crucial in navigating complex tax laws and implementing effective tax practices.
What is the significance of Continuous Transaction Controls (CTC) in the role of an indirect tax manager?
Continuous Transaction Controls (CTC) are significant because they require real-time compliance with tax regulations. By 2030, CTC is expected to become the norm in tax administration, making the indirect tax manager's role even more critical for ensuring tax accuracy from the outset.
How can effective management by an indirect tax manager benefit rural companies?
Effective management by an indirect tax manager can help rural companies optimize their resources and avoid potential legal issues and financial penalties associated with non-compliance.
What skills and focus areas are important for modern indirect tax professionals?
Modern indirect tax professionals should focus on ensuring data accuracy and leveraging technology to transform manual processes into strategic insights. They are not just about processing returns but also fostering a culture of compliance and smart financial planning within the organization.