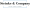Overview
Hey there! Let’s talk about the Net Investment Income Tax, or NIIT for short. This is a 3.8% tax that kicks in on certain investment earnings for individuals, estates, and trusts when their modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) goes above specific thresholds. If you're a small business owner with some investment income, this can really hit your wallet hard!
Understanding NIIT is super important for effective tax planning. Why? Because with a bit of strategic management of your income and deductions, you can actually lighten the load of this tax. So, how are you planning to tackle your taxes this year? Remember, a little knowledge goes a long way!
Introduction
Understanding the ins and outs of the Net Investment Income Tax (NIIT) is super important for small business owners trying to navigate the tricky world of taxes. This 3.8% tax, which came about with the Affordable Care Act, zeroes in on certain investment earnings. And let me tell you, its impact can really shake up your financial strategies. With those tax thresholds creeping up, the real challenge is figuring out how to manage your investment income wisely to keep those tax burdens in check.
So, how can small business owners tweak their financial planning? It’s all about not just coping with this tax but also finding ways to use it to boost profitability. Let's dive in and explore how you can make this tax work for you!
Define Net Investment Income Tax (NIIT)
The Net Investment Earnings Tax is a 3.8% levy that targets specific net investment earnings for individuals, estates, and trusts when their modified adjusted gross earnings (MAGI) exceed certain thresholds. Introduced under the Affordable Care Act in 2013, this tax was designed to help fund healthcare reforms. It covers various forms of passive income, including interest, dividends, capital gains, rental income, and royalties. For small business owners, especially those with investment income, understanding what is NIIT tax is crucial, as it can significantly impact their overall tax burden.
Looking ahead to 2025, the thresholds for the Net Investment Income Tax are set at:
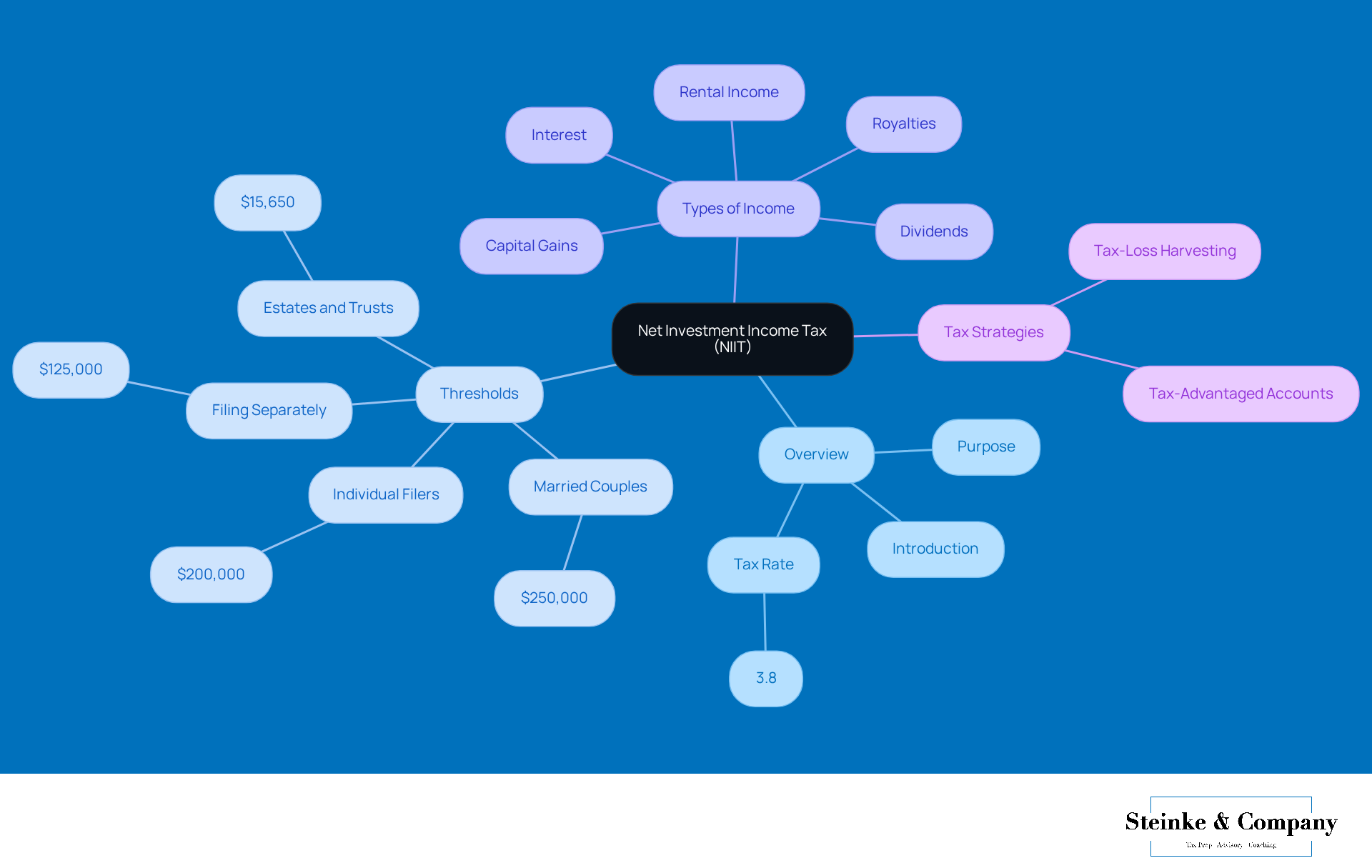
- $250,000 for married couples filing jointly
- $200,000 for individual filers
- $125,000 for those filing separately
- $15,650 for estates and trusts
If a taxpayer's MAGI exceeds these limits, they may face additional tax on the lesser of their net investment earnings or the amount by which their MAGI surpasses the threshold.
Now, for service-oriented businesses, the implications of this tax can be quite significant. Picture a small business owner with substantial investment income—suddenly, their tax bill could skyrocket because of this extra tax. Case studies show that proactive tax planning, like utilizing tax-loss harvesting or contributing to tax-advantaged accounts, can help mitigate exposure to the net investment income tax. By strategically managing their earnings and deductions, small business owners can effectively lower their taxable income and reduce their additional tax liabilities.
It's also worth noting that certain types of income, such as salaries and self-employment income, aren't counted in these calculations. This allows entrepreneurs to focus on maximizing their investment returns. As the tax landscape evolves, staying informed about what is NIIT tax and other relevant tax regulations and their implications is essential for small businesses aiming to manage their tax responsibilities effectively.
Understand the Purpose and Relevance of NIIT
Understanding what is NIIT tax is crucial as it plays an important role in funding Medicare and healthcare initiatives, particularly for higher-income individuals and entities. It ensures that everyone contributes their fair share to the healthcare system. If you're a small business owner, knowing what is NIIT tax is key since it can really affect your investment strategies and overall financial planning. Understanding what is NIIT tax is crucial as it plays a significant role in decisions about asset distribution, company structure, and how you allocate your revenue, making it a key factor for anyone in service-oriented industries.
For instance, if you're running a small business, you might need to tweak your investment strategies to cut down on potential tax liabilities—especially if your adjusted gross income goes over $200,000 for single filers or $250,000 for married couples filing jointly. This might mean strategically allocating your assets to minimize net investment returns, which can help lower your tax exposure.
Now, proactive tax planning can really help you lower your Modified Adjusted Gross Income (MAGI). Think about using rental property depreciation, making charitable contributions, or investing in tax-deferred annuities. These strategies can help you navigate the complexities of understanding what is NIIT tax while boosting your financial results. Plus, understanding how this new tax affects wealth distribution can help you organize your pay and dividends better, ultimately reducing your tax obligations.
Don’t forget, you may need to increase your income tax withholding or estimated taxes because of the extra liability from the net investment income tax to steer clear of penalties. As this new tax initiative continues to shape the financial landscape, it’s vital for small business owners to stay alert and informed about its implications. This way, you can align your financial strategies with the ever-changing tax environment. Staying aware not only helps with compliance but also enhances your ability to reinvest in your business and support long-term growth.

Identify Who is Subject to NIIT and Income Thresholds
Hey there! Let’s discuss what is niit tax. This tax comes into play for individuals, estates, and trusts when their modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) goes over certain limits. For the 2025 tax year, if you’re filing as a single person, your threshold is $200,000. But if you’re married and filing jointly, you get a higher threshold of $250,000. Estates and trusts, however, have a lower threshold of $12,150.
Now, if your income exceeds these thresholds, you might be looking at a 3.8% tax. This applies to the lesser of your net investment income or the amount by which your MAGI exceeds the threshold. It’s super important for small business owners to understand these limits so they can prepare for any tax obligations that might come their way.
And here’s something to keep in mind: the IRS has underpayment penalties if you don’t pay enough tax throughout the year. To avoid those pesky penalties, make sure your estimated tax payments are on point and submitted on time. This proactive approach not only helps you manage your NIIT liabilities but also clarifies what is niit tax, reducing the risk of any underpayment penalties. So, stay ahead of the game and keep your tax compliance strategies sharp!
Break Down Components of Net Investment Income
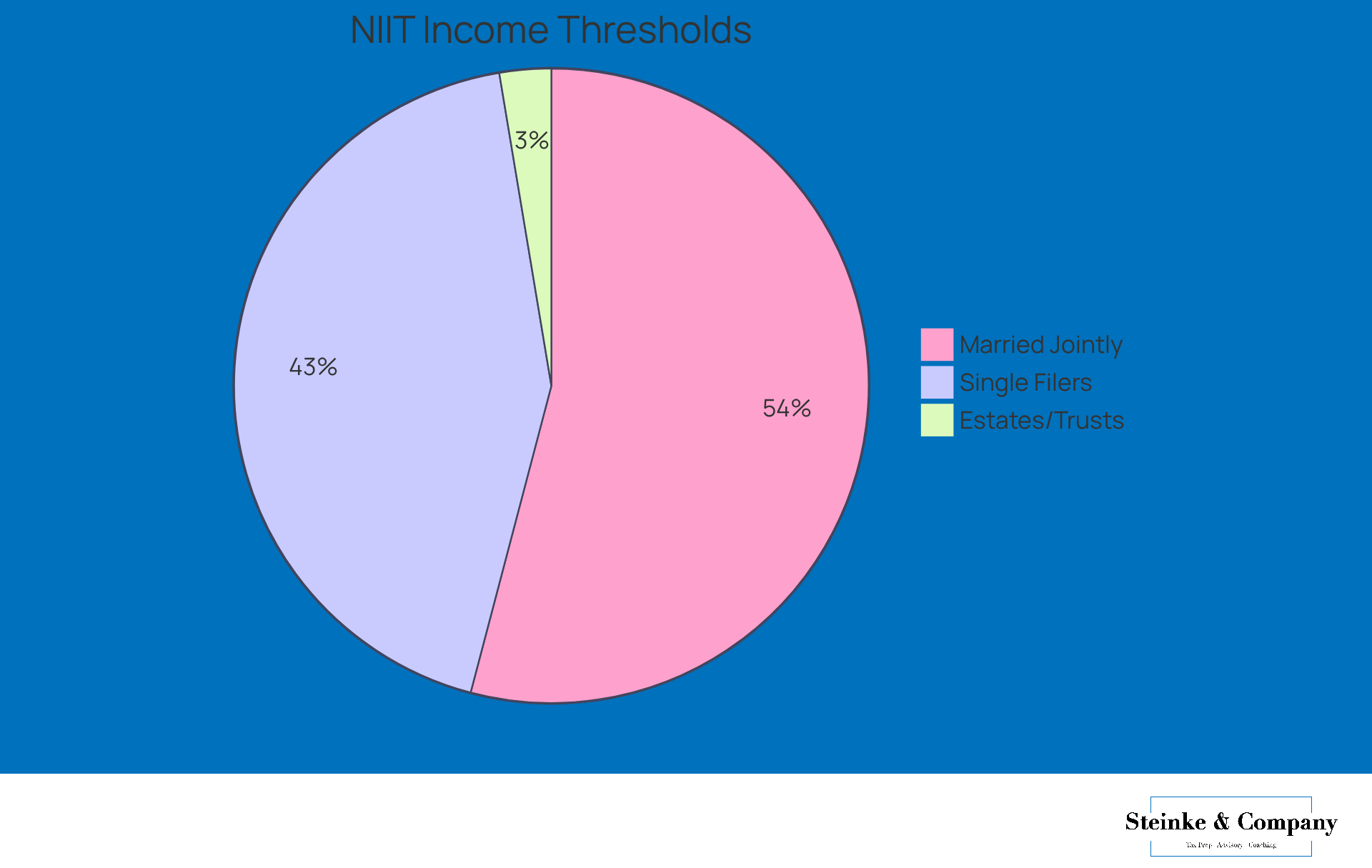
Net investment earnings (NII) cover a variety of income sources, including:
- Interest
- Dividends
- Capital gains
- Rental revenue
- Royalties
This revenue comes from investments in stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and real estate, along with profits from selling these assets. But here’s something small business owners should keep in mind: there are certain exclusions from NII, like wages, self-employment earnings, and tax-exempt interest.
For example, let’s say a married couple has a modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) of $300,000 and $15,000 in net investment income. They would find that the tax applies to the full $15,000 because it’s below the $50,000 threshold calculated from their MAGI. Understanding these nuances helps small business owners strategically assess their investment strategies and potential tax implications, all while aiming for better financial outcomes.
Additionally, many investors might not realize what is NIIT tax, often dubbed a 'stealth tax.' This can lead to some unexpected surprises come tax season! By understanding what is NIIT tax and what counts as NII, small business owners can navigate their financial strategies more effectively and enhance their overall tax planning. So, how are you planning to tackle your investment income this year?
Conclusion
Understanding the Net Investment Income Tax (NIIT) is super important for small business owners, especially if you have a good amount of investment income. This 3.8% tax can really shake up your financial planning and overall tax liability once your modified adjusted gross income goes beyond certain thresholds. By getting a handle on the ins and outs of NIIT, you can tackle your tax responsibilities more effectively and make smarter choices about your investment strategies.
In this article, we’ve highlighted some key points about NIIT, like the income thresholds for different filing statuses, the kinds of income that fall under this tax, and why proactive tax planning is crucial. Think about strategies like tax-loss harvesting, using tax-advantaged accounts, and tweaking your asset allocations to help lessen the financial impact of NIIT. Plus, knowing what counts as net investment income can help you optimize your financial outcomes and avoid those pesky unexpected tax liabilities.
Ultimately, staying in the loop about NIIT and what it means for you is vital for small businesses that want to thrive in today’s complicated tax landscape. By managing your income and tax strategies proactively, you can not only lighten your tax load but also reinvest in your business for long-term success. Embracing this knowledge gives you the power to navigate the ever-changing tax environment with confidence, ensuring you stay compliant and strategically positioned for success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Net Investment Income Tax (NIIT)?
The Net Investment Income Tax is a 3.8% tax that applies to specific net investment earnings for individuals, estates, and trusts when their modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) exceeds certain thresholds.
When was the NIIT introduced and why?
The NIIT was introduced under the Affordable Care Act in 2013 to help fund healthcare reforms.
What types of income are covered by the NIIT?
The NIIT covers various forms of passive income, including interest, dividends, capital gains, rental income, and royalties.
What are the income thresholds for the NIIT in 2025?
The thresholds for the NIIT in 2025 are: - $250,000 for married couples filing jointly - $200,000 for individual filers - $125,000 for those filing separately - $15,650 for estates and trusts.
How is the NIIT calculated for taxpayers exceeding the thresholds?
If a taxpayer's MAGI exceeds the thresholds, the NIIT may apply to the lesser of their net investment earnings or the amount by which their MAGI surpasses the threshold.
How can small business owners manage their exposure to the NIIT?
Small business owners can manage their exposure to the NIIT through proactive tax planning strategies, such as utilizing tax-loss harvesting or contributing to tax-advantaged accounts to lower their taxable income.
Are salaries and self-employment income included in the NIIT calculations?
No, salaries and self-employment income are not counted in the NIIT calculations, allowing entrepreneurs to focus on maximizing their investment returns.
Why is it important for small businesses to stay informed about the NIIT?
Staying informed about the NIIT and other relevant tax regulations is essential for small businesses to effectively manage their tax responsibilities and mitigate potential tax liabilities.