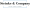Introduction
Navigating the world of tax incentives can feel a bit like wandering through a maze, right? This is especially true for small businesses trying to make their mark in a competitive landscape. Enter the General Business Credit (GBC) - a game-changer that offers a variety of tax credits designed to ease financial pressures and spark growth and innovation. But with over 30 different credits out there, how can businesses tap into these opportunities to really make the most of them?
In this article, we’ll dive into what the GBC is all about, explore its various types, and discuss who’s eligible. Plus, we’ll look at the significant impact it can have on a company’s financial health and long-term success. So, let’s get started!
Define the General Business Credit
What is the general business credit (GBC)? It is a useful tax measure that assists businesses in reducing their federal income tax bills through a variety of individual tax incentives. What is the general business credit? It is not just one credit; it actually includes over 30 different credits designed to encourage specific business activities, like research and development, energy efficiency upgrades, and smart hiring practices. For instance, small businesses can benefit from the Work Opportunity Tax Credit (WOTC), which offers up to $2,400 for each new full-time employee. That’s a great way to lighten the tax load!
To understand what is the general business credit, companies need to have average yearly gross receipts of no more than $50 million to qualify, which opens the door for many smaller businesses. The total value of these credits is summarized on IRS Form 3800, where all the different incentives claimed by a business in a tax year are recorded. This is super important because it helps small businesses manage their tax responsibilities effectively, freeing up crucial cash for reinvestment and growth. Looking ahead to 2025, the GBC continues to play a significant role in helping small businesses understand what is the general business credit and how to use it for their tax obligations, with many firms taking advantage of these incentives to boost their financial stability.
Now, here’s something to keep in mind: the GBC is nonrefundable. This means it can only reduce your tax liability to zero, and any unused credits, which relate to what is the general business credit, can be carried back one year or forward for up to 20 years. Recent updates to IRS Form 3800 reflect changes in tax laws, so it’s really important for businesses to stay in the loop about how to claim these credits.
As small business owners tackle the tricky world of tax compliance, it’s also wise to be aware of strategies to dodge underpayment penalties. One effective method is using safe harbor payments, which let businesses prepay a minimum amount of their tax obligation to help avoid those pesky penalties. Plus, understanding the de minimis exception can be a lifesaver. This rule says that if your total tax liability minus withholdings and credits is less than $1,000, you’re off the hook for penalties. How great is that?
Understanding what is the general business credit and its related forms can really help entrepreneurs maximize their tax benefits, ultimately leading to a stronger economic landscape. And don’t forget to keep an eye on how reduced COVID-19 tax benefits might affect your tax refunds; being informed can really sharpen your financial strategies moving forward.

Contextualize the Importance of the General Business Credit
For small businesses, especially those in rural areas facing tough economic times, understanding what is the general business credit (GBC) is super important. It works like this: for every dollar you spend, you get a dollar off your tax bill. This means companies can keep more of their earnings, which they can then reinvest into their operations, employee training, or even expansion plans.
For example, imagine a small manufacturing company that qualifies for various incentives. They could see a big drop in their tax obligations, freeing up cash to upgrade their machinery or hire new staff. Pretty neat, right? This credit not only gives immediate financial relief but also encourages businesses to think long-term. It allows them to invest in sustainable practices and growth opportunities.
Fast forward to 2025, and the impact of the GBC on small business growth is becoming more recognized. Many firms are reinvesting their tax savings to boost their operational capabilities and stay competitive in the market. Overall, what is the general business credit serves as a vital tool for helping small businesses thrive and grow, aligning perfectly with their long-term goals. So, if you're a small business owner, have you thought about how the GBC could benefit you?
Identify Types of Tax Credits Within the General Business Credit
When it comes to general commercial credit, there’s a whole range of individual tax credits out there, each designed to encourage specific activities. Let’s take a look at some of the standout examples:
- Investment Credit: This one’s all about encouraging businesses to invest in certain types of property, like renewable energy systems. Not only can this significantly cut down tax liabilities, but it also supports sustainable practices-talk about a win-win!
- Work Opportunity Credit: Here’s a great incentive for hiring individuals from targeted groups who face significant barriers to employment. It’s a fantastic way to support workforce development while giving financial assistance to businesses that participate.
- Research Credit: If your business is involved in qualified research activities aimed at creating new or improved products or processes, this credit can help. Companies can claim a percentage of their research spending, which is pretty neat!
- Low-Income Housing Credit: This credit incentivizes the development of affordable housing projects, tackling housing shortages while offering tax benefits to developers. It’s a crucial step in making housing more accessible.
Now, each of these incentives comes with its own eligibility requirements and application process. To make the most of their benefits under the general enterprise incentive (GEI), companies need to understand what is the general business credit and navigate these challenges. A key point to remember is what is the general business credit, as businesses must submit IRS Form 3800 to claim several tax incentives during the current tax year. This form consolidates various allowances into one, making calculations a bit simpler. Plus, the general credit can be carried back one year or forward 20 years, which adds some flexibility to tax planning.
Understanding these nuances is super important for small businesses looking to boost their tax strategies. As Steinke and Company points out, professional tax preparation and planning services can help ensure compliance and minimize surprises, allowing businesses to focus on growth. And don’t forget, keeping track of paystubs and maintaining proper tax records is essential for financial stability and compliance. It really underscores the importance of strategic financial planning.
As the xendoo Team puts it, "Tax incentives reduce the amount you owe," which really highlights the financial perks of taking advantage of these benefits. So, why not dive in and explore how these credits can work for you?

Outline Eligibility Requirements for Claiming the General Business Credit
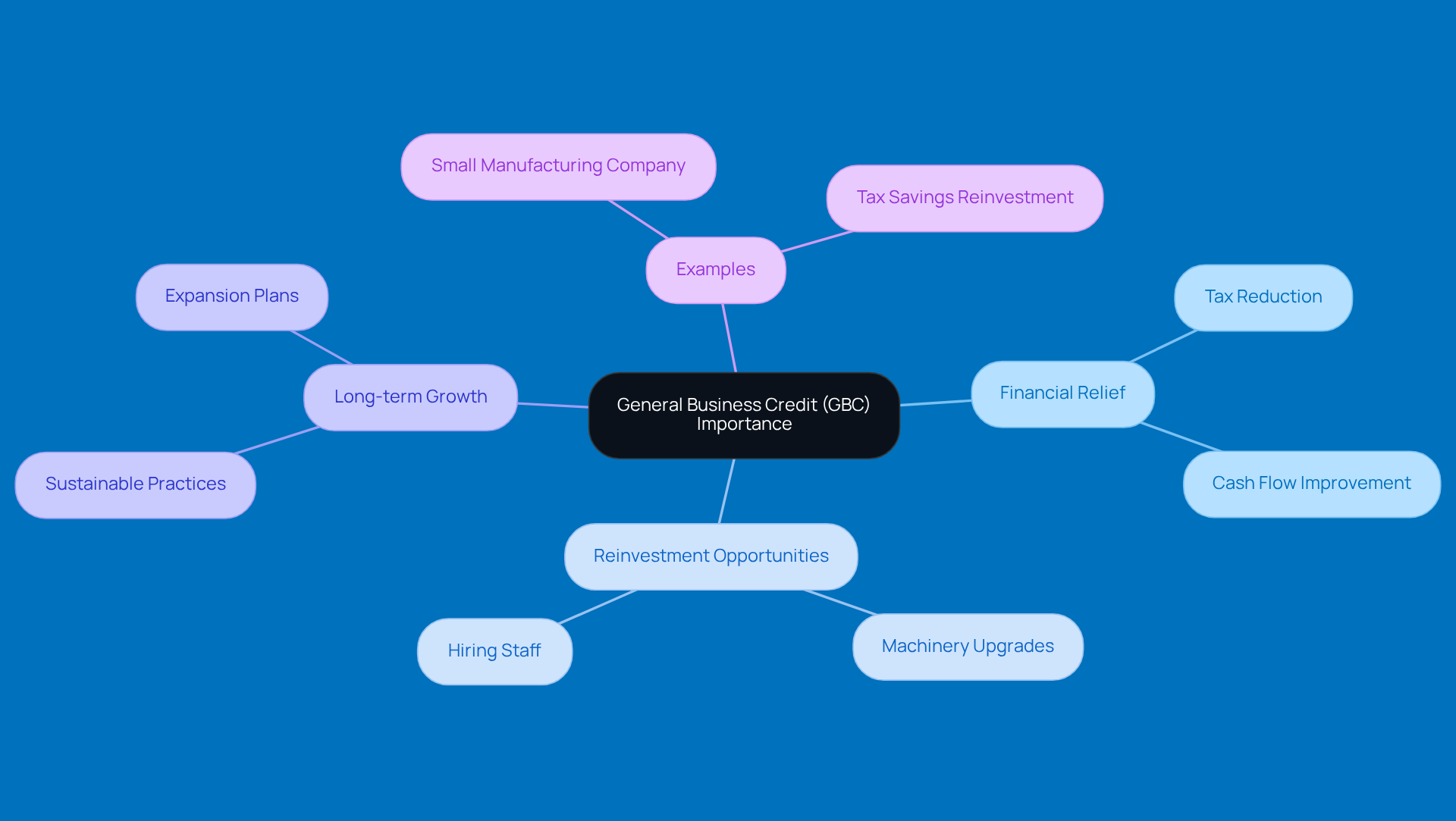
If you're looking to snag the General Business Incentive, there are some eligibility requirements you need to keep in mind. These can change depending on the specific incentives you're after, but here are the main ones:
- Business Structure: You can be a sole proprietor, a partnership, an S corporation, or a C corporation. Just a heads up-publicly traded companies usually can’t tap into this funding.
- Gross Receipts: Your business's average annual gross receipts over the last three years shouldn’t go over $50 million. This cap is in place to make sure the funding mainly helps out smaller businesses.
- Qualified Activities: You’ll need to be involved in activities that align with the benefits you’re claiming. This could mean diving into research projects, investing in energy-efficient property, or hiring from specific target groups.
Now, don’t forget that you’ll need to file IRS Form 3800 along with any relevant source forms to claim those credits accurately. For entrepreneurs, understanding what is the general business credit is super important. It not only helps you stay compliant but can also boost your tax benefits. For instance, small businesses that navigate these criteria successfully can significantly reduce their federal income tax obligations. So, it’s wise to stay updated on the latest tax rules and consider seeking professional advice when necessary.
Also, a quick reminder for small business owners: if you don’t meet your tax obligations throughout the year, you might face underpayment penalties. The IRS expects you to pay at least 90% of your current year’s tax liability or 100% of the previous year’s tax to dodge those penalties. With recent changes in tax benefits following the end of COVID-19 relief measures, getting a grip on these dynamics is crucial for effective tax planning and compliance.
So, how are you planning to tackle your tax strategy this year?
Conclusion
Understanding the general business credit (GBC) is super important for small businesses looking to make the most of their tax obligations. This tax measure isn’t just about saving money; it’s also a way for businesses to reinvest in themselves, which helps them grow and thrive. By tapping into the various credits under the GBC umbrella, companies can manage their tax responsibilities better and boost their financial health.
Throughout this article, we’ve highlighted why the GBC matters, showcasing its different components like the Work Opportunity Tax Credit, Investment Credit, and Research Credit. Each of these credits has its own role, offering incentives for things like job creation, innovation, and energy efficiency. Plus, we’ve talked about the eligibility requirements, stressing how crucial it is to understand IRS Form 3800 for claiming these credits correctly.
So, in a nutshell, the general business credit is a key resource for small businesses trying to navigate the tricky world of tax compliance while maximizing their financial benefits. By staying in the loop about available credits and knowing how to use them wisely, entrepreneurs can not only cut down on their tax bills but also set their businesses up for long-term success. Engaging with tax pros and keeping up with tax regulations will only enhance your ability to take advantage of these incentives, ultimately helping to create a stronger economic landscape for small businesses.
What steps will you take to explore these credits further?
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the general business credit (GBC)?
The general business credit (GBC) is a tax measure that helps businesses reduce their federal income tax bills through various individual tax incentives, encompassing over 30 different credits aimed at encouraging specific business activities.
What types of activities do the credits under the general business credit support?
The credits under the GBC support activities such as research and development, energy efficiency upgrades, and smart hiring practices.
Can small businesses benefit from the general business credit?
Yes, small businesses can benefit from the GBC, such as through the Work Opportunity Tax Credit (WOTC), which offers up to $2,400 for each new full-time employee.
What are the eligibility requirements for businesses to qualify for the general business credit?
To qualify for the GBC, businesses must have average yearly gross receipts of no more than $50 million.
How is the total value of the general business credit summarized?
The total value of the credits is summarized on IRS Form 3800, where all different incentives claimed by a business in a tax year are recorded.
Is the general business credit refundable?
No, the GBC is nonrefundable, meaning it can only reduce tax liability to zero, and any unused credits can be carried back one year or forward for up to 20 years.
What recent updates are important for businesses regarding the general business credit?
Recent updates to IRS Form 3800 reflect changes in tax laws, making it important for businesses to stay informed about how to claim these credits.
What is one strategy businesses can use to avoid underpayment penalties?
One effective strategy is to use safe harbor payments, which allow businesses to prepay a minimum amount of their tax obligation to help avoid underpayment penalties.
What is the de minimis exception in relation to tax liability?
The de minimis exception states that if a business's total tax liability minus withholdings and credits is less than $1,000, they are exempt from penalties.
How might COVID-19 tax benefits affect businesses?
Businesses should keep an eye on how reduced COVID-19 tax benefits might impact their tax refunds, as being informed can help sharpen their financial strategies.